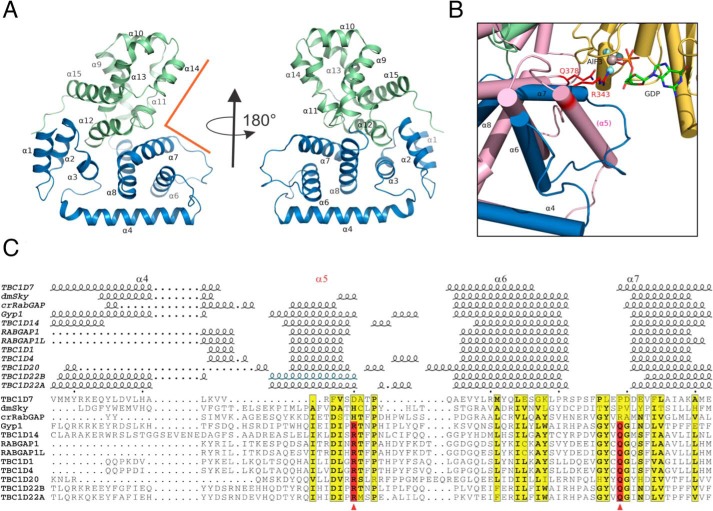
Figure 2.
Structure of TBC1D7 and comparison with other TBC domains. A, overview of TBC1D7 structure. 15 α-helices were labeled based on the structure of yeast Gyp1 (89). The N-subdomain (α1–α8) is colored in blue, and the C-subdomain (α9–α15) is colored in light green. The rectangular groove that binds to Rab GTPase in Gyp1 is indicated using orange lines. B, an enlarged view of the region between α4 and α7 of TBC1D7 and compared with Gyp1 (salmon color) and Rab33 (yellow). Helix α5 is missing in TBC1D7. The dual-finger Arg-343/Gln-378 critical for Gyp1 RabGAP activity and the GDP molecule are shown as sticks. The AlF3 molecule is shown as a sphere. C, structure-based alignment of 12 known TBC domain structures of the region between α4 and α7. The active sites of the dual finger are indicated using red arrowheads. The structures are D. melanogaster Skywalker (dmSky, PDB code 5HJN), yeast Gyp1 (2G77), C. reinhardtii RabGAP (crRabGAP, 4P17), RABGAP1 (4NC6), RABGAP1L (3HZJ), TBC1D1 (3QYE), TBC1D4 (3QYB), TBC1D7 (3QWL), TBC1D14 (2QQ8), TBC1D20 (4HL4), TBC1D22A (2QFZ), TBC1D22B (3DZX). The α5 helix of the TBC1D22B crystal structure is presumed disordered or missing due to the use of protease and is indicated based on the high sequence identity to that of TBC1D22A.