Figure 4.
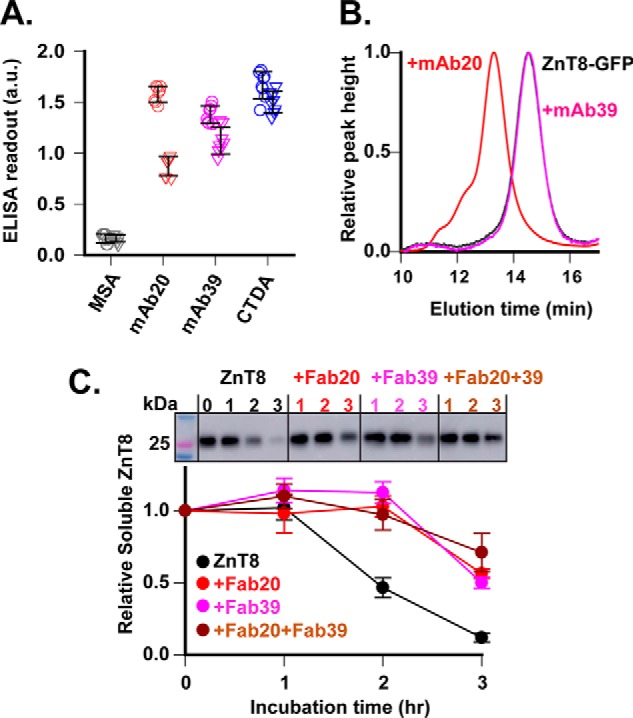
Stabilizing ZnT8 folding by mAb binding. A, mAb binding to folded or denatured ZnT8. ZnT8-His in detergent micelles was immobilized to a Ni-NTA plate in replication without SDS denaturation. ELISAs against denatured (triangle) and nondenatured ZnT8 (circle) were compared for mAb20 and mAb39 as indicated. CTDA and MSA were used as a positive and negative control, respectively. Error bars, S.D. B, mAb binding to folded ZnT8-GFP in detergent micelles. mAb20 or mAb39 was mixed with ZnT8-GFP, and then the binding mixture was analyzed by size-exclusion HPLC with GFP fluorescence detection. Note that mAb20 shifted the unbound ZnT8-GFP peak (black) leftward to a mAb20–ZnT8-GFP position (red), whereas mAb39 did not cause peak shift (magenta). C, protection of ZnT8 unfolding. Aliquots of ZnT8 in detergent micelles were incubated with Fab20 (red), Fab39 (magenta), or Fab20 + Fab39 (brown). Free ZnT8 was used as a control (black). After a designated time of heat denaturation as indicated, protein aggregates were removed by ultracentrifugation, and the amount of remaining ZnT8 in the supernatant was detected by mAb20 immunoblotting (top). Error bars, S.E. of six independent densitometric measurements of one representative experiment using ImageJ. a.u., arbitrary units.
