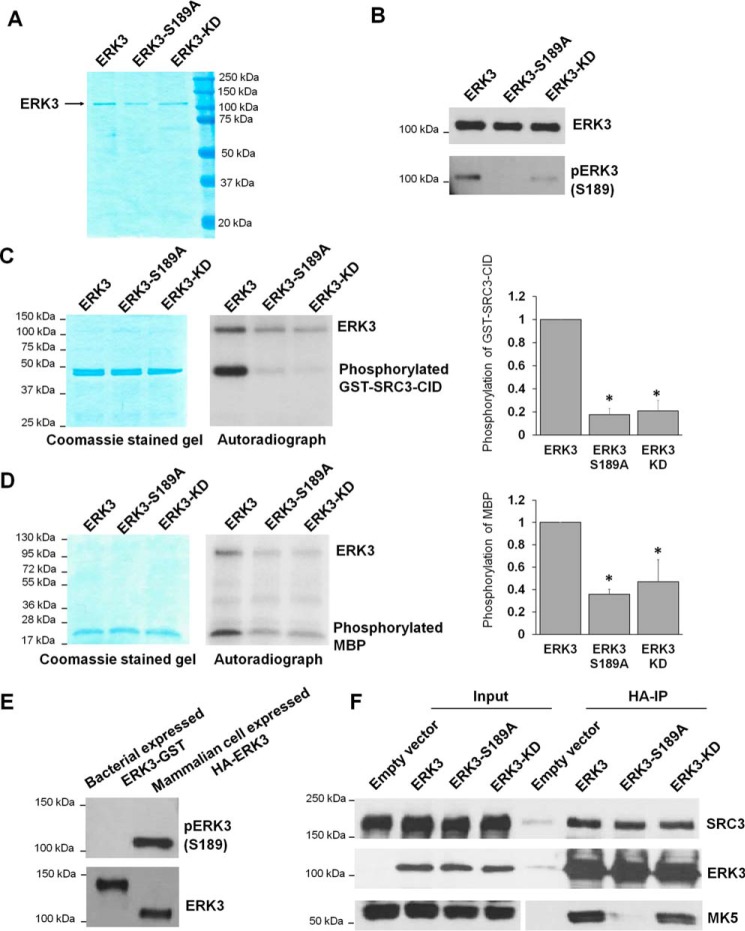
Figure 6.
The S189A mutation decreases the in vitro kinase activity of ERK3 protein expressed and immunoprecipitated from 293T cells. A, purification of WT or mutant ERK3 proteins by immunoprecipitation from 293T cells. 293T cells were transfected with the HA-ERK3, HA-ERK3-S189A, or HA-ERK3-KD plasmid, followed by immunoprecipitation of exogenously expressed ERK3 proteins using HA Ab–conjugated agarose beads and elution of the proteins with HA peptide. The purified proteins (300 ng each) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE, followed by Coomassie Blue staining. B, Western blot analysis of proteins purified from mammalian cells using anti-ERK3 and anti-phsopho-ERK3 (Ser189) antibodies. C and D, in vitro kinase assay for WT or mutant HA-ERK3 proteins immunoprecipitated from mammalian cells using GST-SRC3-CID (C) or MBP (D) as substrates. The assays were performed by incubating 100 ng of WT or mutant ERK3, as indicated, together with 1 μg of recombinant protein substrate in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP. Total protein levels of substrates in the reactions are shown by Coomassie staining (left panels). ERK3 proteins are barely seen in the Coomassie-stained gels because of their small amounts (100 ng each). Phosphorylation of the substrates was detected by autoradiography (center panels). Quantification of substrate phosphorylation by WT or mutant ERK3 proteins is shown in the right panels. For the purpose of comparison, the normalized phosphorylation level of substrates by WT ERK3 was arbitrarily set as 1.0. The bar graphs represent the mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments. *, p < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA. E, Western blot analysis of His-ERK3-GST recombinant protein expressed in bacteria and HA-ERK3 protein expressed in 293T cells using anti-phospho-ERK3 (Ser189) and anti-ERK3 antibodies. F, activation loop phosphorylation and kinase activity are not required for interaction of ERK3 with its substrate SRC3 in cells. 293T cells were co-transfected with SRC3 and an HA tag–expressing empty vector, WT HA-ERK3, or mutant HA-ERK3 plasmids, as indicated. Two days post-transfection, cells were lysed, and the interactions of ERK3 with SRC3 and MK5 were analyzed by co-immunoprecipitation using HA Ab–conjugated beads, followed by Western blotting using antibodies against ERK3, SRC3, and MK5.