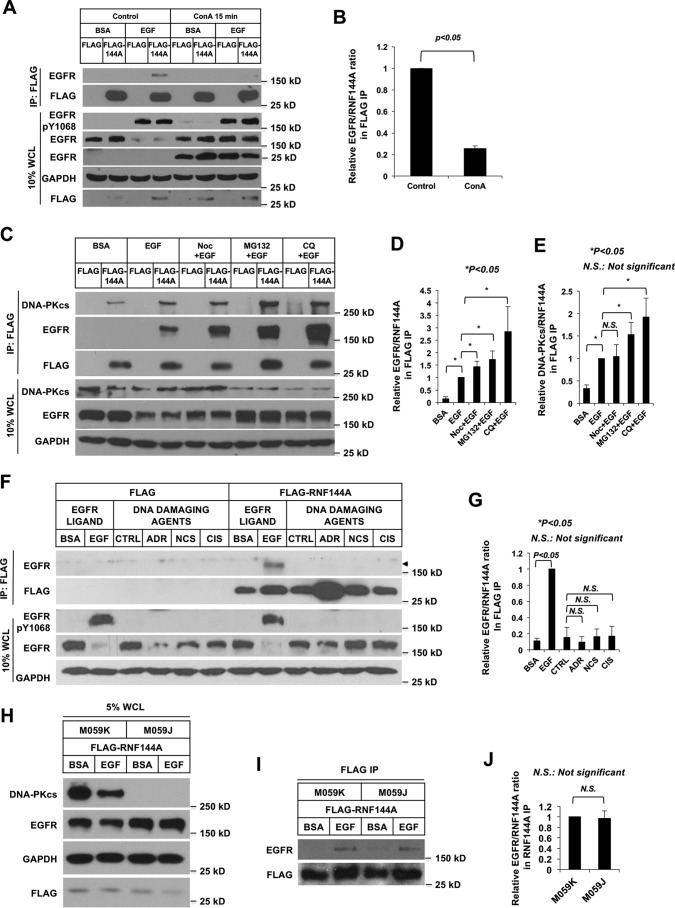
Figure 3.
The interaction of RNF144A with EGFR requires endocytosis and is independent of its interaction with DNA-PKcs nor is RNF144A-EGFR association induced by DNA damage. A and B, endocytosis inhibitor, ConA, reduced the EGF-induced RNF144A-EGFR interaction. C–E, EGF induced both RNF144A-EGFR and RNF144A–DNA-PKcs interaction. Noc, MG132, and lysosome inhibitor, chloroquine (CQ), could further enhance the accumulation of the RNF144A–EGFR complex. Cells were pretreated with the indicated inhibitors for 30 min prior to EGF stimulation. F and G, DNA damaging agents, adriamycin (ADR), neocarzinostatin (NCS), and cisplatin (CIS) could not induce RNF144A-EGFR association. H–J, EGF-induced RNF144-EGFR interaction in both DNA-PK-proficient (M059K) and DNA-PK-deficient (M059J) cells. B, D–E, G, and J are quantifications of EGFR/RNF144A or DNA-PKcs/RNF144A ratio in the FLAG IP from A, C, F, and I, respectively. All quantification data represent mean ± S.D. from three biological replicates. *, p < 0.05; N.S., not significant. FLAG, FLAG-tagged empty vector; BSA, 0.1% BSA in serum-free medium; EGF, EGF stimulation; CTRL is a control solution of DNA damaging agents.