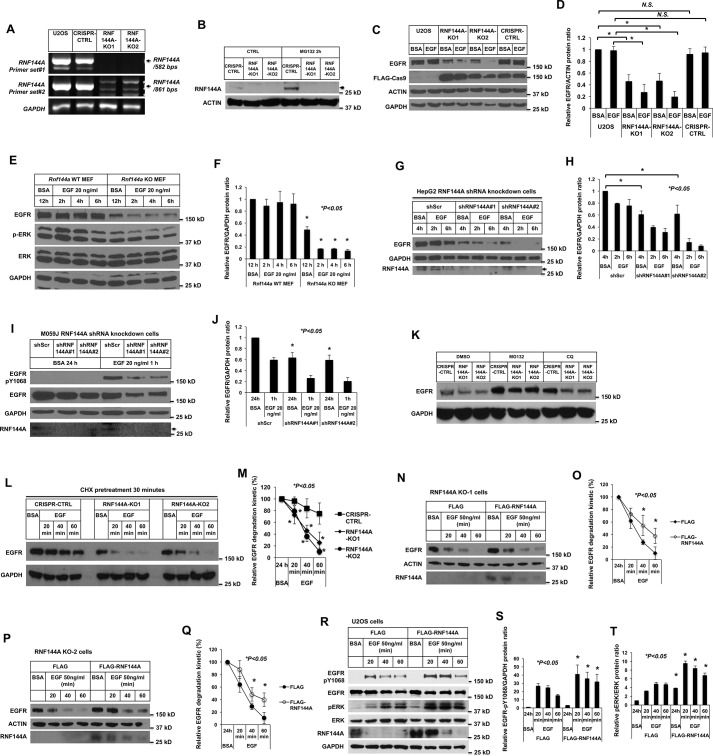
Figure 5.
RNF144A is important for maintaining EGFR protein and the EGF/EGFR signaling. A and B, generation of two independent RNF144A stable knockout clones in U2OS cells using the CRISPR/Cas9 system. DNA-agarose gel (1%) shows that the RNF144A transcript was undetectable in two different primer sets even after 50 cycles of RT-PCR amplification. Primer set (# 1) RNF144A-407F/RNF144A-988R and (# 2) RNF144A-749F/RNF144A-1609R (A). Western blot analysis shows the expression of RNF144A in the CRISPR-CTRL system, but not in the two RNF144A knockout cell lines. The proteasome inhibitor MG132 could only further accumulate RNF144A in CRISPR-CTRL cells (B). The arrow indicates RNF144A bands. C–F, Western blot analysis shows that knockout of RNF144A reduced the EGFR protein level in U2OS cells (C and D) and in the transformed MEFs (E and F). Quantitation of Western blots by ImageJ software from three independent experiments of C or E is shown in D or F, respectively. *, p < 0.05; N.S., not significant. G–J, Western blot analysis shows that knockdown of RNF144A reduced EGFR protein level in HepG2 cells (G) and M059J cells (I). The arrows in G and I indicate RNF144A bands. Depletion of RNF144A in these two cell lines were also independently confirmed by qRT-PCR assays (Fig. S9). H and J, quantitation of Western blots by ImageJ software from three independent experiments of G or I is shown in H or J, respectively. K, Western blot analysis shows that proteasome inhibitor (MG132) and lysosome inhibitor (CQ) could partially rescue EGFR protein levels from the RNF144A knockout U2OS cells. L and M, depletion of RNF144A promoted EGF-induced degradation of EGFR protein under inhibition of newly synthesized EGFR by cycloheximide (CHX) treatment. The data shown represent mean ± S.D. (n = 3 biological replicates for each condition). *, p < 0.05; N.S., not significant. N–Q, reintroduction of exogenous RNF144A attenuated EGF-stimulated EGFR degradation in both RNF144A KO cells. O and Q, quantitation of Western blots by ImageJ software from three experiments of N or P is shown in O or Q, respectively. R–T, overexpression of WT RNF144A decreased EGFR degradation and induced the EGF-dependent phosphorylation of ERK Thr202/Tyr204 by EGF stimulation. S and T are quantitations of EGFR-Tyr(P)1068/GAPDH ratio and pERK/ERK ratio from R; all quantification data represent mean ± S.D. from three independent experiments. *, p < 0.05; N.S., not significant.