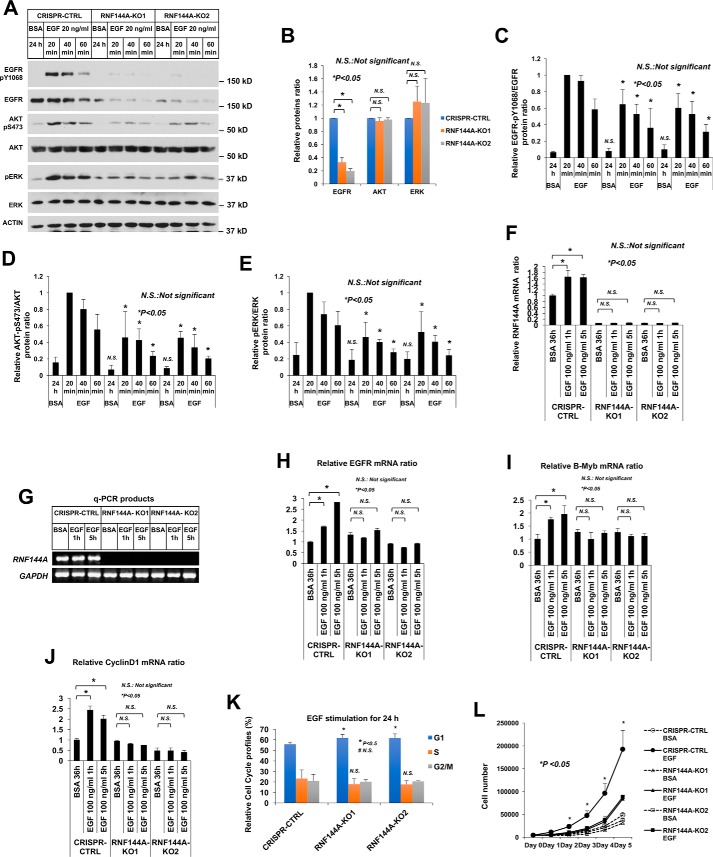
Figure 7.
Knockout of RNF144A inhibits EGF-dependent gene activation and cell cycle progression. A–E, knockout of RNF144A reduced the EGF-dependent phosphorylation of EGFR-Tyr1068 (C), AKT-Ser473 (D), and ERK-Thr202/Tyr204 (E). B, relative proteins ratio shows knockout of RNF144A only reduced EGFR protein level, but not AKT or ERK protein levels. All quantification data represent mean ± S.D. from three biological replicates. *, p < 0.05; N.S., not significant. F–J, real-time quantitative RT-PCR analysis shows that EGF induced the expression of RNF144A (F), EGFR (H), B-Myb (I), and Cyclin D1 (J) in the RNF144A CRISPR-CTRL cells but not in the two RNF144A knockout cell lines. G, DNA-agarose gel shows the RNF144A transcript could not be detected even after 40 cycles of qPCR amplification from F. Results were normalized to GAPDH levels and the mean ± S.D. (n = 3) are expressed relative to the expression of genes in CRISPR control cells. K, cell cycle profile analysis shows that depletion of RNF144A slightly increased G1 phase population upon 24 h of EGF treatment. L, cell proliferation analysis shows that RNF144A was required for a full response of EGF-dependent cell proliferation. Data in K and L represent mean ± S.D. from three biological replicates.