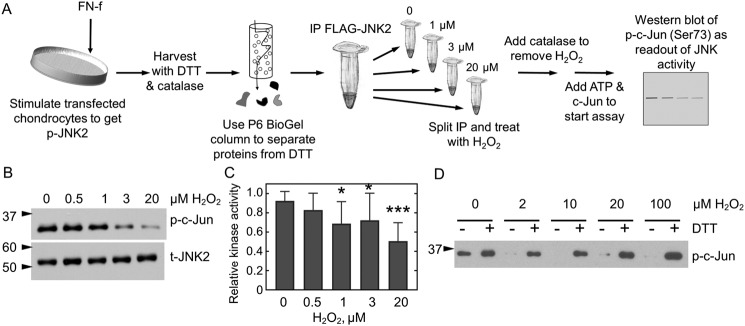
Figure 3.
JNK2 activity is reversibly inhibited by H2O2. A, JNK2 kinase assay. FLAG-JNK2α2–expressing chondrocytes were treated with FN-f to stimulate JNK phosphorylation. Cellular proteins were reduced prior to affinity capture of JNK2 with anti-FLAG magnetic beads. A single immunoprecipitation (IP) was then split into multiple fractions and treated or not with various amounts of H2O2 for 10 min prior to the addition of catalase to remove excess H2O2. Protein kinase A activity was then initiated by the addition of prereduced c-Jun and ATP, and JNK2 activity was measured as a function of c-Jun phosphorylation. B, WT FLAG-JNK2 was immunoprecipitated from 60 μg of lysate and then split into multiple tubes prior to treatment with 0, 0.5, 1, 3, or 20 μm H2O2 for 10 min, and kinase activity was measured as described in A. C, shown is the mean and S.D. (error bars) for n = 14 replicates for protein expressed from chondrocytes harvested from different donors. The p value for one-way ANOVA comparing different H2O2 concentrations is <0.0001. Dunnett's multiple comparison test was used to identify H2O2 concentrations with significantly different JNK kinase activity from untreated protein; *, p value <0.05; ***, p value <0.005. D, JNK2 inhibition is reversible by reduction. Active, phosphorylated JNK2α2 was purchased from SignalChem and treated or not with H2O2 and then catalase as described above. Each sample was then split in half. DTT was added to one half (+), and an equal amount of water (−) was added to the second prior to the addition of c-Jun and ATP. p, phospho; t, total.