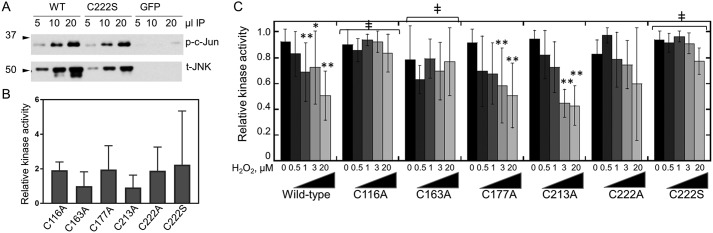
Figure 5.
Sensitivity of JNK2 cysteine mutants to H2O2-mediated inhibition. A, FLAG-tagged WT JNK2α2, C222S JNK2, or a FLAG-GFP control construct were immunoprecipitated (IP) from FN-f–stimulated chondrocytes, and kinase activity was measured as a function of c-Jun phosphorylation (p) as described in Fig. 3A except that no H2O2 was added and assays included 2 mm DTT. Blots were stripped and reprobed with an antibody to detect the total (t) amount of JNK2 protein added to each assay. All constructs were transfected into the same donor-derived cell line, and all treatments and analysis were performed side by side on the same day. B, c-Jun kinase activity of reduced JNK2 mutants does not differ significantly from WT JNK2. Shown are mean and S.D. (error bars) for the kinase activity for each mutant compared with the activity of untreated WT protein from the same donor-derived cells. Mutant and WT activity assays were performed on the same day and analyzed on the same gel. All values are normalized to the signal for total JNK2 protein. Shown are the mean and S.D. One-way ANOVA indicated no significant difference between the samples (p value = 0.42). C, the immunoprecipitated JNK2 cysteine mutants were assayed for JNK2 kinase activity after treatment with increasing concentrations of H2O2 as described in Fig. 2A. Shown are the mean and S.D. (error bars) for a minimum of four biological replicates for each mutant. Two-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's post hoc comparison was used to identify mutant constructs that were significantly less inhibited by H2O2 than WT JNK2 with ‡ indicating a p value <0.05. Asterisks represent significant differences: *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.005 relative to untreated control for the same variant.