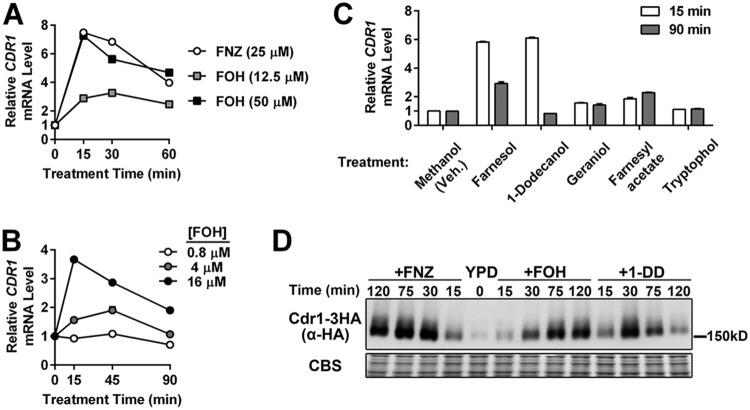
FIG 1.
CDR1 induction by farnesol and 1-dodecanol treatment. (A) RT-qPCR analysis of CDR1 mRNA expression in a C. albicans wild-type strain (yLM167) grown in YPD and treated with farnesol (FOH) or fluphenazine (FNZ). CDR1 basal expression (mRNA level prior to treatment; 0 min) was set to 1 to calculate the relative CDR1 level across conditions. ACT1 level was used as an internal reference. Results from one representative experiment were presented by the means and standard deviations (values may not be large enough to give a visible error bar) of two qPCR measurements on the same set of cDNA samples. (B) RT-qPCR analysis of CDR1 mRNA expression induced by increasing concentrations of FOH. CDR1 expression, in the absence of treatment, in the tested strain (yLM167) was set to 1. (C) RT-qPCR analysis of changes in CDR1 expression upon exposure to molecules structurally or functionally related to FOH. Each compound tested (or an equal volume of methanol [vehicle]) was added into log-phase cultures of a wild-type strain (yLM167) at a final concentration of 50 μM. The CDR1 mRNA level in the methanol-treated samples (15 min) was set to 1. (D) Immunoblot analysis of whole-cell extracts made from a strain expressing C-terminally 3×HA-tagged Cdr1 (yLM505) treated with FNZ (25 μM), FOH (50 μM), or 1-DD (50 μM) for the indicated amount of time. Extracts were resolved on a 6% SDS-PAGE gel and probed by an α-HA antibody or stained by Coomassie blue (CBS) as a loading control.