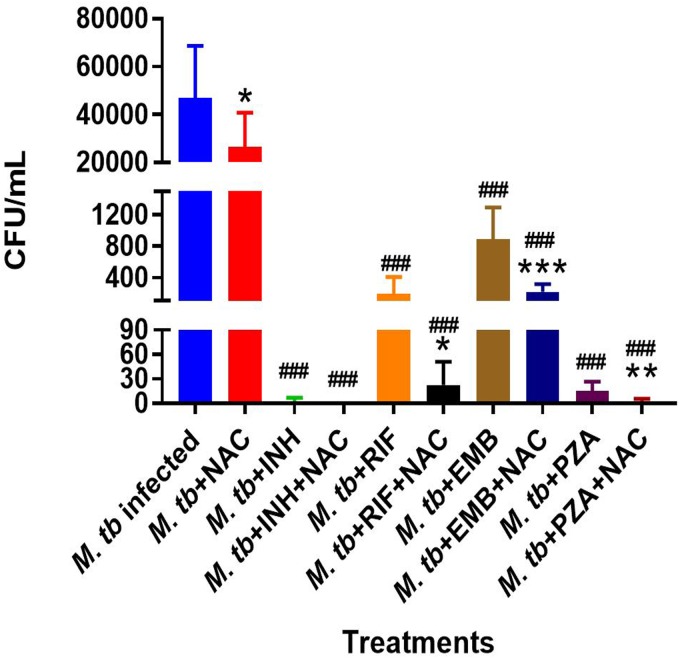
FIG 2.
Survival of M. tuberculosis inside macrophages treated with first-line antibiotics in the presence and absence of NAC. THP-1 cells were cultured in a medium of RPMI and 10% FBS and allowed to differentiate into macrophages by addition of PMA at a concentration of 10 ng/ml. There was a significant decrease in bacterial numbers when M. tuberculosis-infected macrophages were treated with NAC. INH plus NAC treatment resulted in the clearance of M. tuberculosis infection, whereas treatment with INH only did not. There was a significant reduction in the bacterial numbers when THP-1 cells were treated with RIF plus NAC compared to the numbers when they were treated with RIF only. We also observed a significant reduction in the bacterial numbers when THP-1 cells were treated with EMB plus NAC compared to the numbers when they were treated with EMB only. Treatment of M. tuberculosis-infected macrophages with PZA plus NAC resulted in a significant reduction in bacterial numbers compared to those obtained with treatment with PZA only. Data represent the means ± SE from 6 trials. *, P < 0.05 when comparing the antibiotic plus NAC to the antibiotic alone or infected NAC to infected control. **, P < 0.005 when comparing the antibiotic plus NAC to the antibiotic alone or infected NAC to infected control. ***, P < 0.0005 when comparing the antibiotic plus NAC to the antibiotic alone or infected NAC to infected control. ###, P < 0.0005 when comparing each antibiotic category to the infected control.