FIG 7.
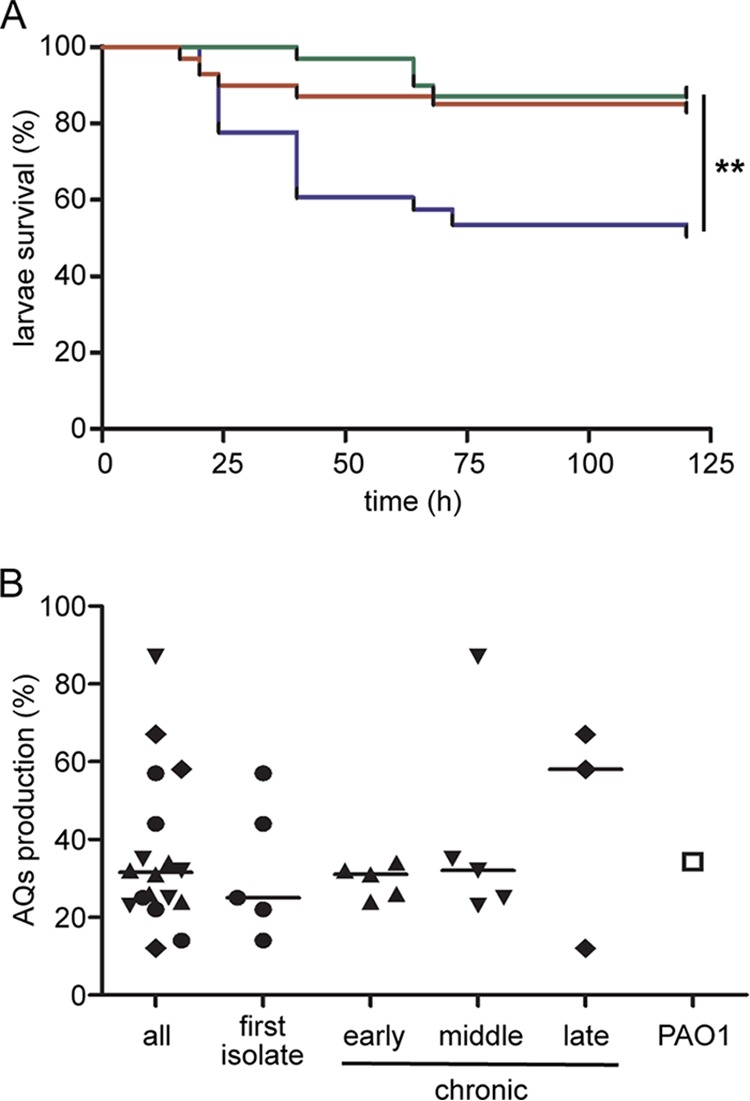
Clofoctol displays an antivirulence effect in vivo and inhibits the pqs QS system in P. aeruginosa CF clinical isolates. (A) Kaplan-Meier plot shows the percentage survival of G. mellonella larvae inoculated with P. aeruginosa PAO1 (blue line), with PAO1 and clofoctol at a final concentration of 100 μM (red line), or with ΔpqsR mutant (green line). The mean survival rate calculated from four independent experiments performed on at least 30 larvae per condition is reported. **, P = 0.0033 for PAO1 versus PAO1 plus clofoctol and P = 0.0016 for PAO1 versus ΔpqsR mutant (ANOVA). (B) Dot plot showing the inhibition of AQ production in P. aeruginosa CF isolates (filled symbols) and P. aeruginosa PAO1 (open square) treated with 100 μM clofoctol, relative to the untreated samples, which were considered 100%. Black lines represent median values: all, 31.4%; first isolate, 25.2%; early chronic, 31.1%; middle chronic, 32.1%; and late chronic, 57.8%. The AQ production in treated PAO1 cultures was 34.3% relative to untreated PAO1. Differences between the median values are not statistically significant. Mean results from three independent experiments are reported.
