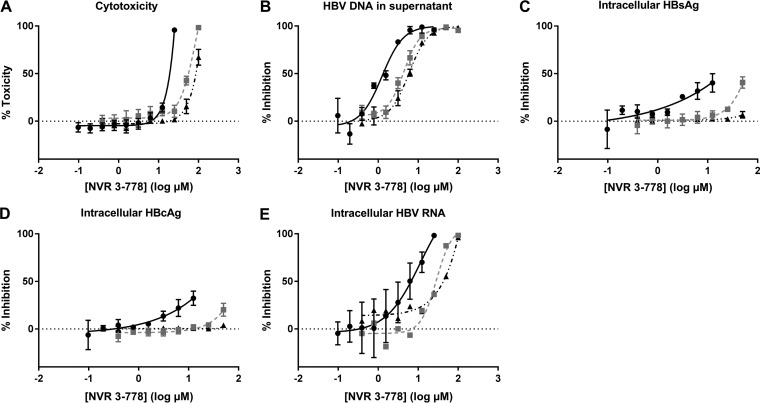
FIG 4.
Cell cytotoxicity and anti-HBV effect of NVR 3-778 on HBV DNA in the supernatant and on intracellular HBsAg, HBcAg, and HBV RNA. NVR 3-778 was added together with the viral inoculum until day 8. HBV-infected PHHs were incubated with a 2-fold dilution series of NVR 3-778 in HCM without plasma proteins (●) or in HCM spiked with either 4.3% BSA–0.07% hA1GP (■) or 8% BSA–0.07% hA1GP (▲). (A) Cell cytotoxicity was assessed by ATP content after incubation of HBV-infected PHHs with NVR 3-778. Percent toxicity was related to the ATP content of untreated PHHs cultured in the corresponding HCM. (B) HBV DNA production in the cell culture supernatant was quantified by qPCR. Percent inhibition was compared to level of HBV DNA produced by untreated cells cultured in the corresponding HCM. (C) Percentage of HBsAg-positive cells was quantified by IF. Percent inhibition was compared to the percentage of HBsAg-positive cells in untreated cells cultured in the corresponding HCM. (D) Percentage of HBcAg-positive cells was quantified by IF. Percent inhibition was compared to the percentage of HBcAg-positive cells in untreated cells cultured in the corresponding HCM. (E) Intracellular HBV RNA was quantified by qPCR. Percent inhibition was compared to the HBV RNA quantity in untreated cells cultured in the corresponding HCM. All data represent the means of three or more independent experiments ± SEM.