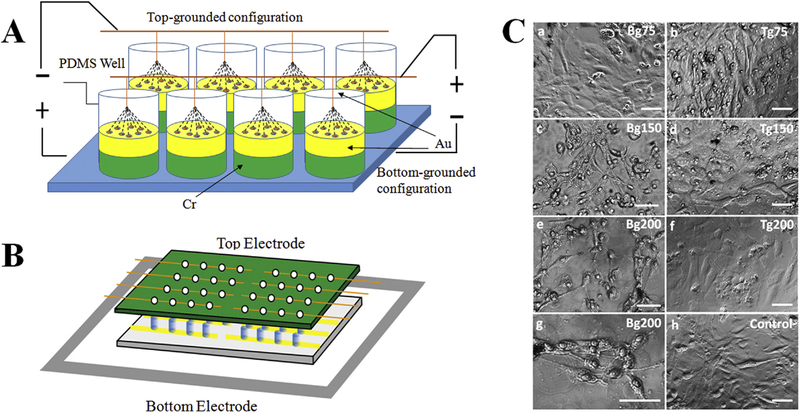
Fig. 1.
(A) Illustration of the electrostimulation platform, which permits easy and simultaneous modulation of multiple parameters such as field polarity, electrical potential, pulsing frequency, and stimulation duration, to deliver adjustable electrical outputs to cells in individual wells. (B) Side view of stimulation set up. Each condition has one group of 4 electrically connected wells. Top electrodes are replaced with clean sealing film when no stimulation is applied. (C) Phase images of NCSCs after stimulated with 1-Hz 50-ms pulses for 24 h at different potential gradients. Cells were stimulated with bottom-grounded (Bg) configuration (a, c, e, g) or top-grounded (Tg) configuration (b, d, f) at 75, 150 and 200 mV/ mm potential in comparison with cells without electrostimulation (h). (g) shows a higher magnification image of (e). Scale bars represent 100 μm.