Figure 2.
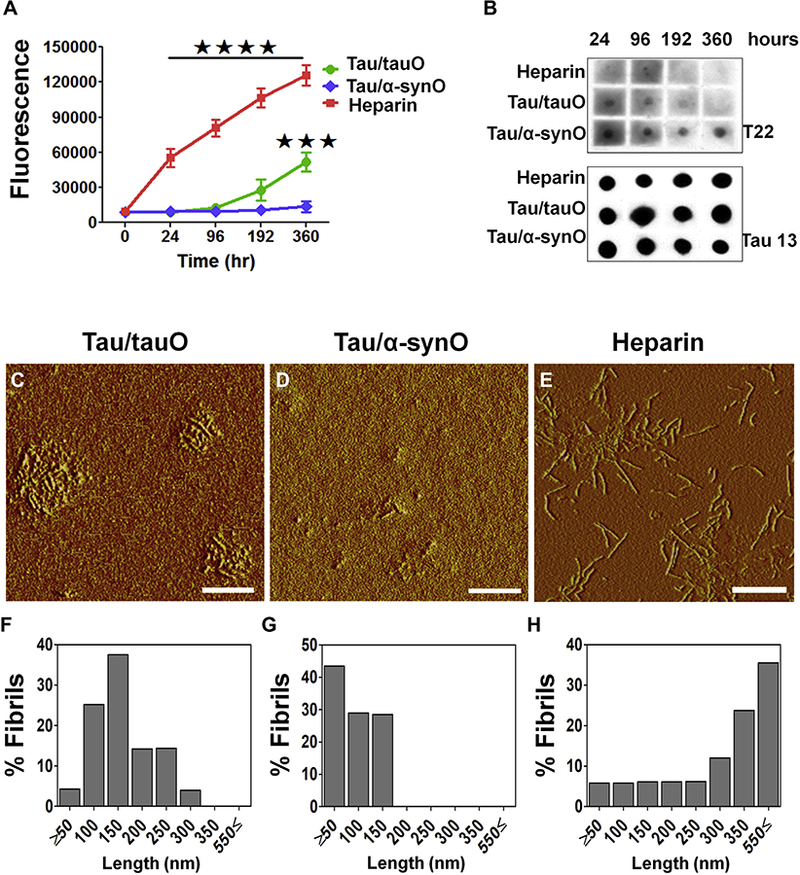
Seeds of α-synuclein shift the tau aggregation pathway, extending lifespan of tau toxic conformation. (A) Kinetic analyses of recombinant tau protein (8 μM) incubated in phosphate-buffered saline (pH 7.2) with either preformed oligomeric tau (tauO; green line) or α-synuclein (α-synO; blue line) at a ratio of 1:140 (weight/weight) or 10 μM of heparin (red) at 22°C for 360 hours. A tau strain induced by α-synO evades fibril formation (blue line), whereas tau readily fibrillizes in the presence of inducers, such as heparin (red line) or seeds of preformed tau oligomers (green line). Bars represent the mean and SEM (****p < .0001, ***p < .001; n = 3 independent experiments; two-way analysis ofvariance, Bonferroni post hoc multiple comparisons test). (B) Dot blot analyses oftauO at different time points using T22 and Tau13antibodies. Both seeds of preformed tauO (Tau/tauO) and heparin induced tau fibril formation, while cross-seeded tau (Tau/α-synO) remains oligomeric. Atomic force microscopy images of tau aggregates induced by (C) preformed tauO (Tau/tauO), (D) α-synO (Tau/α-synO), and (E) heparin. (F–H) Graphs represent the length distribution of tau aggregates. Scale bar = 400 nm.
