Figure 4.
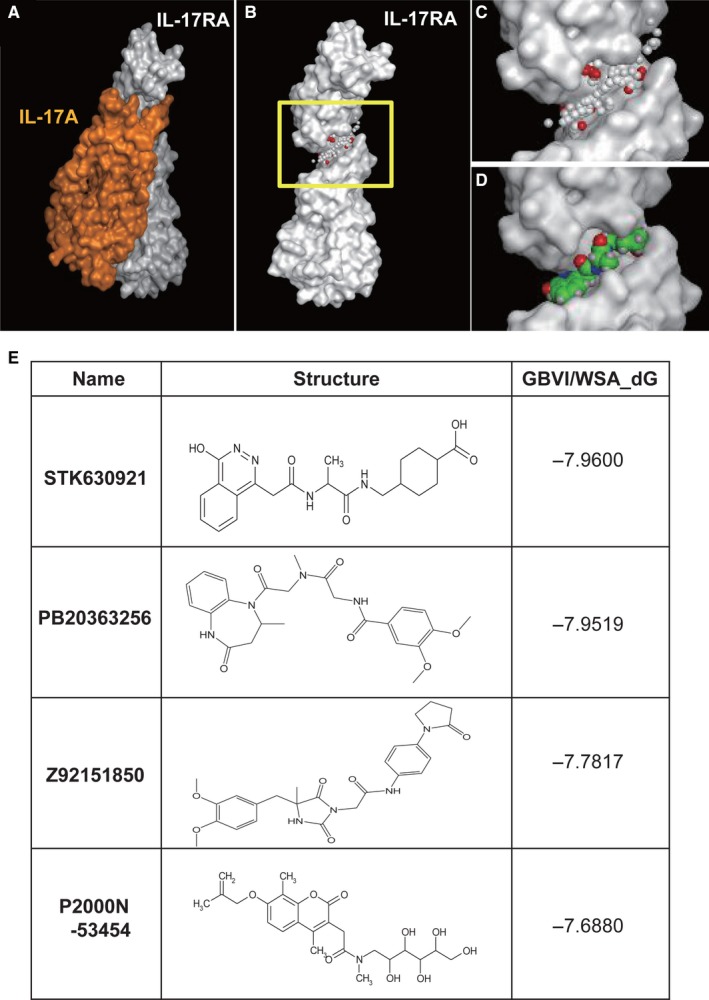
The structures of IL‐17A, IL‐17RA and small‐molecule inhibitors. A, X‐ray structure of IL‐17A bound to IL‐17RA. Molecular surface of a complex between IL‐17A (orange) and IL‐17RA (white). B, Molecular surface of IL‐17RA. The yellow boxed region is the binding site. C, The magnified view of the binding site (yellow boxed region in B). The cleft where a cluster of small spheres (alpha spheres) is localized represents the binding site for IL‐17A. White and red alpha spheres represent hydrophobic and hydrophilic pseudo atoms. D, Binding mode of STK630921 at the biding site of IL‐17A. STK630921 is depicted by a space‐filling model. Carbon, oxygen, nitrogen and hydrogen atoms are green, red, blue and white, respectively. E, Chemical structures of small‐molecule inhibitors for IL‐17A–IL‐17RA
