Figure 3.
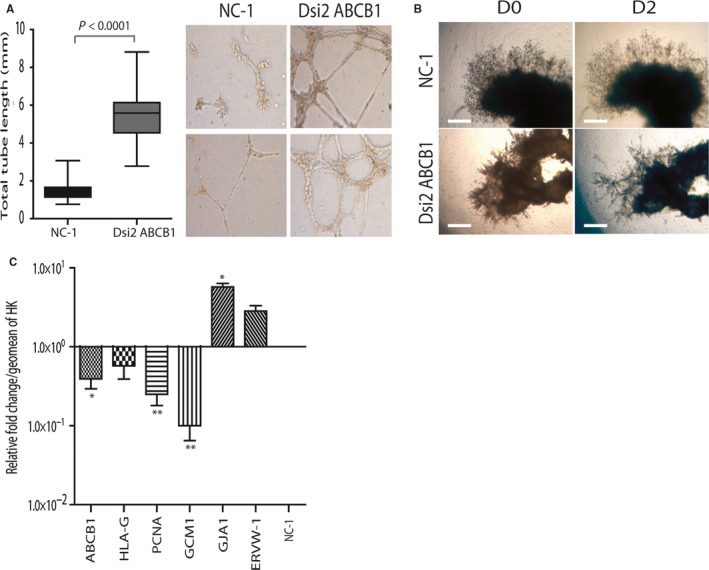
ABCB1 silencing induces tube formation and fusion markers in primary EVT: A, Representative images of two of three independent tube formation experiments (N1 and N2). HTR8/SV neo cells untreated or transfected with either NC‐1 or Dsi2 ABCB1 were seeded in Matrigel‐coated plates and incubated overnight. Silencing of ABCB1 induced a robust and rapid formation of an extensive tubular network as compared to either NC‐1 or untreated controls. Graph shows total tube length over triplicate images per well (P < 0.0001 vs NC‐1 control). B, Established EVT outgrowths (5‐7w) were transfected with either NC‐1 (top panels) or Dsi2 ABCB1 (lower panels) and cultured for 48 h. Explant morphology shows that silencing of ABCB1 promotes tubule formation in the EVT outgrowth (n = 6). C, Bar graph showing the change in EVT and fusion marker mRNA levels in primary EVT cell columns following 48 h of ABCB1 silencing as determined by qPCR. Fusion markers GJA1 and ERVW‐1 were increased on treatment with DSi2 ABCB1 (*P < 0.05 GJA1 only). ABCB1 levels decreased as expected (P < 0.05) as did PCNA and GCM‐1 (**P < 0.001, n = 3). Data are expressed as the relative fold change from NC‐1 controls at 1.0. Data were normalized as in Figure 2A. Data were analysed using one‐way ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc testing or the paired Student's t test in C. Graphs show the mean and standard deviation. Scale bars = 400 μm
