Figure 1.
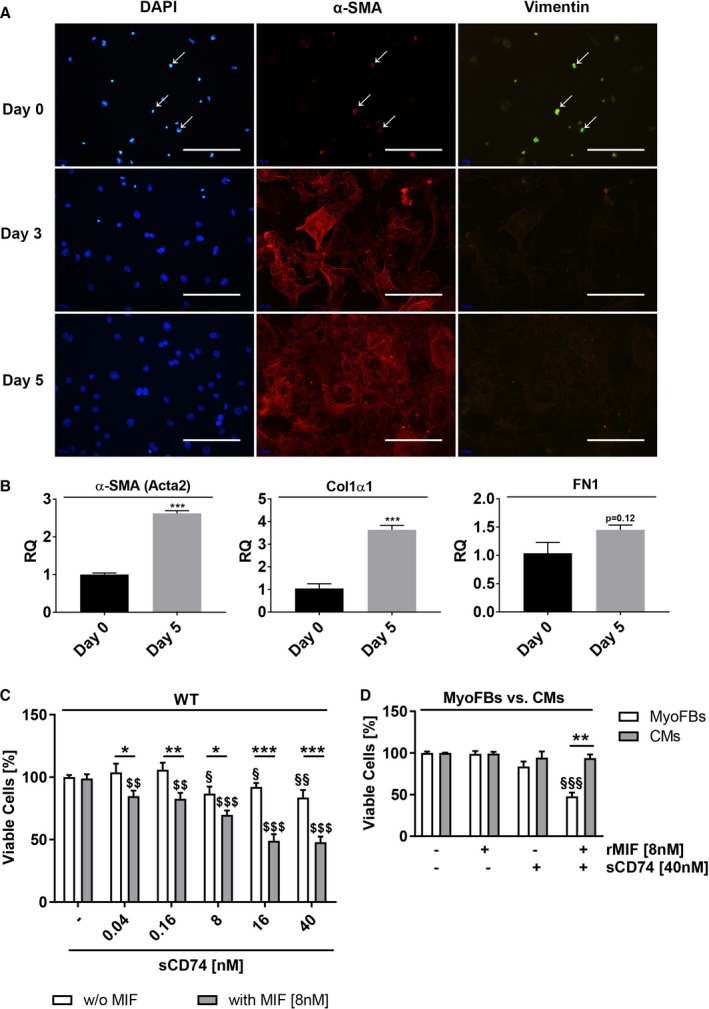
Co‐treatment with sCD74 and MIF promotes cell death in cardiac myofibroblasts. A, Primary isolated cardiac fibroblasts were co‐stained with the fibroblast marker, vimentin (green), the myofibroblast marker, α‐smooth muscle actin (α‐SMA) (red), and nuclei were stained with 4′,6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole (DAPI; blue) after 0 (5 hours), 3, and 5 days in culture. Size bar, 200 μm. B, mRNA level of α‐SMA, collagen 1α1 (Col1α1), and fibronectin 1 (FN1) were determined 5 hours (day 0) and 5 days after plating by the RT‐qPCR method. Data represent mean±SEM of 3 independent experiments and were analyzed with a 2‐tailed, unpaired t test. ***P<0.001 vs day 0. C, Cardiac myofibroblasts (MyoFBs) isolated from hearts of wild‐type C57BL/6J (WT) mice were treated with increasing concentrations of sCD74 (0, 0.04, 0.16, 8, 16, and 40 nmol/L) without or with rMIF (8 nmol/L). After 24 hours, cells were stained with trypan blue and cell numbers were assessed. Data were analyzed with a 2‐tailed, unpaired t test and represent means±SEM of at least 7 independent experiments. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001 without (w/o) MIF vs with MIF respectively; § P<0.05; §§ P<0.01 vs untreated control respectively; $$ P<0.01; $ P<0.001 vs MIF control respectively. D, Murine cardiomyocytes (CMs) were stimulated with 40 nmol/L of sCD74 in the absence or presence of 8 nmol/L of rMIF for 24 hours, followed by trypan blue staining. Percentage of survival of CMs was compared with MyoFBs. Data represent mean±SEM of 6 independent experiments and were analyzed with a 2‐tailed, unpaired t test with multiple correction (n=9). $$$ P<0.001 vs control of MyoFBs; **P<0.01 MyoFBs vs CMs. MIF indicates macrophage migration inhibitory factor; RQ indicates relative quantity; rMIF, recombinant MIF; sCD74, soluble CD74.
