Figure 7.
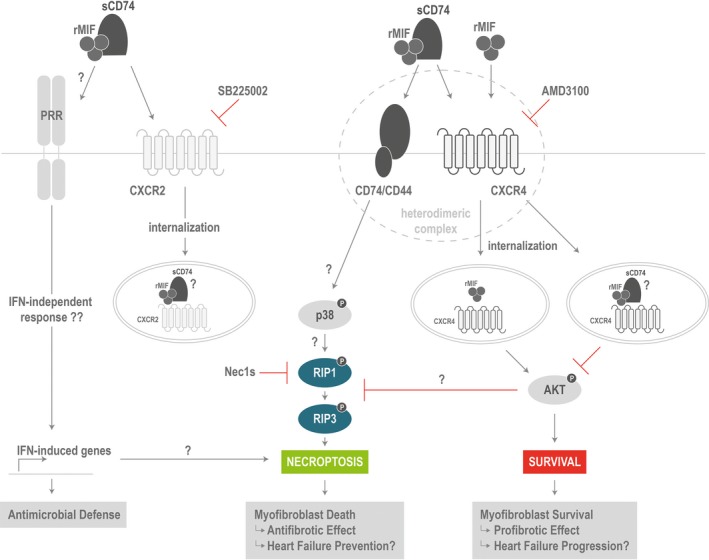
Proposed model of molecular switch between the profibrotic MIF/CXCR4 signal and antifibrotic MIF/CD74 signal. Recombinant MIF triggers CXCR4 internalization, which requires the presence of CD74. Subsequently, MIF/CXCR4 axis mediates survival by AKT activation. Although sCD74/MIF still induces CXCR4 (and CXCR2) internalization, AKT signaling is disturbed. However, the CXCR4/AKT axis seems to be important to suppress cell death. As soon as MIF‐mediated CXCR4 activation is inhibited, signaling by CD74 predominates resulting in RIP1 and RIP3 phosphorylation and, finally, necroptosis. Furthermore, sCD74/MIF seems to be recognized in a DAMP‐like manner to activate components typical for the antimicrobial defense system, such as type 1 interferon (IFN)‐induced genes. AKT indicates protein kinase B; CXCR, C‐X‐C chemokine receptor; DAMP, danger‐associated molecular pattern; MIF, macrophage migration inhibitory factor; RIP1/3, receptor‐interacting serine/threonine‐protein kinases 1 and 3; rMIF, recombinant MIF; sCD74, soluble CD74.
