Table 2.
The structure, cells, category, source, and mechanism of typical polyphenols compounds on inhibiting VSMCs proliferation and migration.
| Compound name | Structure | Cells and animals | Category | Sources | Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salvianolic acid B |
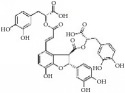
|
NeCs; HAECs and cholesterol-fed rabbits; rTASMCs and rats balloon injury |
Polyphenol | Salvia miltiorrhiza | (1) p53 ↑; NeCs apoptosis, (2) ROS ↓; LDL oxidation ↓; lipid deposition ↓, (3) PCNA ↓; NQO1 ↓; via Nrf2-ARE-NQO1 pathway |
| Caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) |
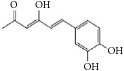
|
rASMCs | Polyphenol | Honeybee propolis | Blocking G0/1 to S phase; pp38 ↑;HiF1α ↑;HO-1 ↑ |
| Hispolon |
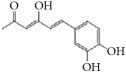
|
rTA-A10-VSMCs | Polyphenol | Phellinus linteus | MMP2 ↓;MMP9 ↓; TIMP-1 ↑;TIMP-2 ↑; pFAK ↓; pERK1/2 ↓;PI3K/AKT ↓ |
| [6]-shogaol |
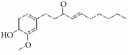
|
rASMCs | Phenols | Zingiber officinale | Inhibit DNA synthesis; activation of (Nrf2)/HO-1 pathway |
| Resveratrol |
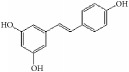
|
ncTASMCs; mASMCs |
Polyphenol | Widely (grapes, blueberries, raspberries, and etc.) | c-Src ↓, Rac1 ↓, cdc42 ↓, IRS-1 ↓, MEKK1 ↓, MEKK4 ↓; p-Src; pFAK ↓; pAKT ↓; pERK1/2 ↓ |
| Lithospermic acid |
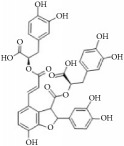
|
rTASMCs | Polyphenol | Salvia miltiorrhiza | ROS ↓; pERK1/2 ↓; cyclin D1 ↓; arresting cell cycle progression at the G1 phase; MMP9 ↓ |
| Magnolol |
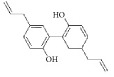
|
Cholesterol-fed rabbits; rVSMCs; rats balloon injury |
Polyphenol | Magnolia officinalis | (1) MCP-1 ↓, (2) Reduce collagen type I deposition; β1-integrin ↓;pFAK ↓;pMLC20 ↓; RhoA ↓;Cdc42 ↓ |
| Obovatol |
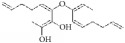
|
rASMCs; rats balloon injury | Biphenol | Magnolia obovata | Blocks the cell cycle in G1 phase; CDKs ↓;p21cip1 ↓ |
| Curcumin |
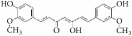
|
rTASMCs; rabbit artery injury; VECs; RAECs |
Phenols | Curcuma longa | (1) Inhibits PDGF Receptor Binding; PDGFr ↓; pERK1/2 ↓; pAkt ↓, (2) P-selectin ↓; E-selectin ↓; GPIIb/GPIIIa ↓, (3) MMP2 ↓; pRas ↓; MEK1/2 ↓; NF-κB p65 ↓, (4) Curcumin protects aortic endothelial cells; eNOS ↑; caveolin-1 ↓; |
