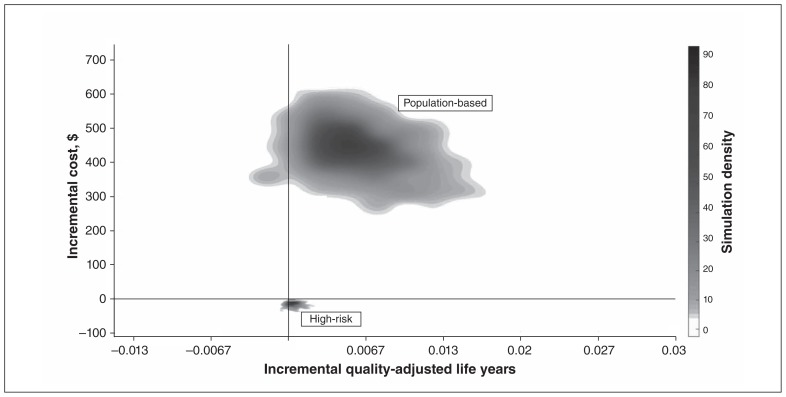
Figure 2:
Cost-effectiveness plane of 1000 Markov simulations in both a high-risk approach and a population-based approach assuming a rate of effectiveness of diabetic foot ulcer prevention of 30%. Most of the simulations conclude that telemedicine screening results in a gain of quality-adjusted life years, whereas only the high-risk screening strategy results in cost savings to the health care system.