Figure 1.
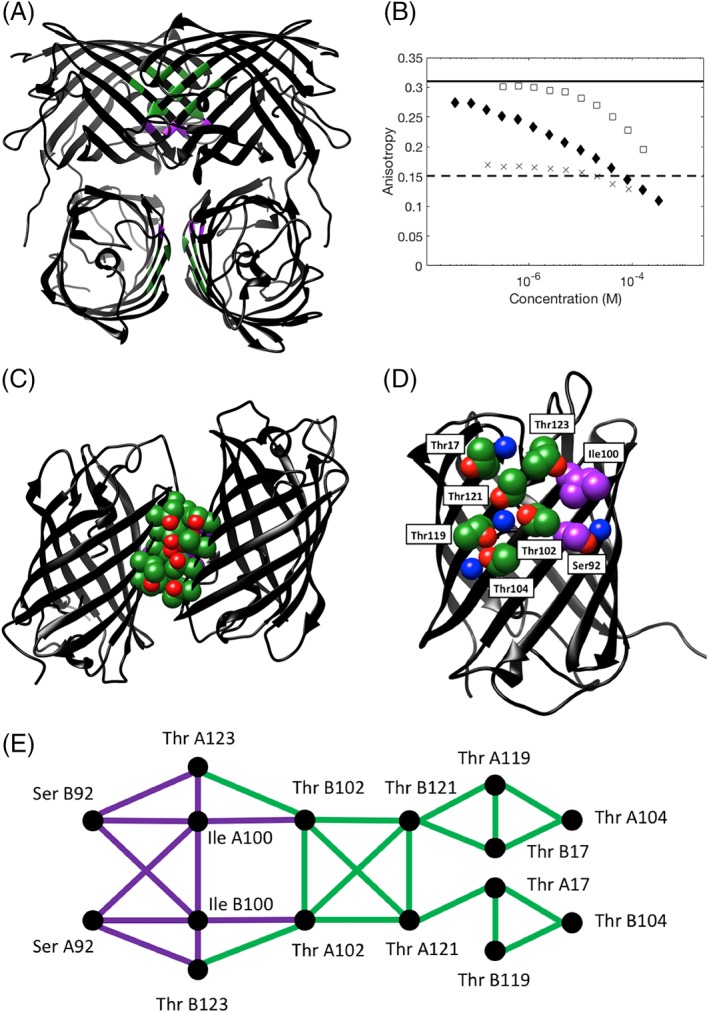
Crystal structure of the tetrameric Thr zipper protein, illustrating the positions of key interface residues and data for the oligomeric state from anisotropy experiments. (A) Ribbon representation of the Thr zipper tetramer structure with interface residues colored by residue type (green = Thr, purple = non‐Thr interface core residue). (B) Fluorescence anisotropy of Azami Green mutants, as a function of protein concentration. Each of the three mutants of Azami Green was serially diluted from its stock solution and then the anisotropy was measured: D121T (crosses), R119TD121TV123T (solid diamonds), and R119DD121TV123T (open squares). The solid line shows the expected anisotropy for an Azami Green monomer, the dashed line shows the expected anisotropy for an Azami Green tetramer. (C) Ribbon representation of the Thr zipper structure with two of the monomers shown to illustrate the dimer interface. (D) A view of the Thr zipper monomer, showing the positions of the key interface residues, and high occupancy water molecules. In both C and D, the side chains of interface residues are shown in space filling representation: green and red (oxygen) = Thr; purple = non‐Thr interface core residue, blue = a water molecule. (E) Interaction network of the key interface residues for chains A and B based on hard sphere interactions. Thr–Thr contacts are shown in green, other contacts in purple. The interaction graph for the interface residues on chains C and D has an identical network topology.
