Figure 8.
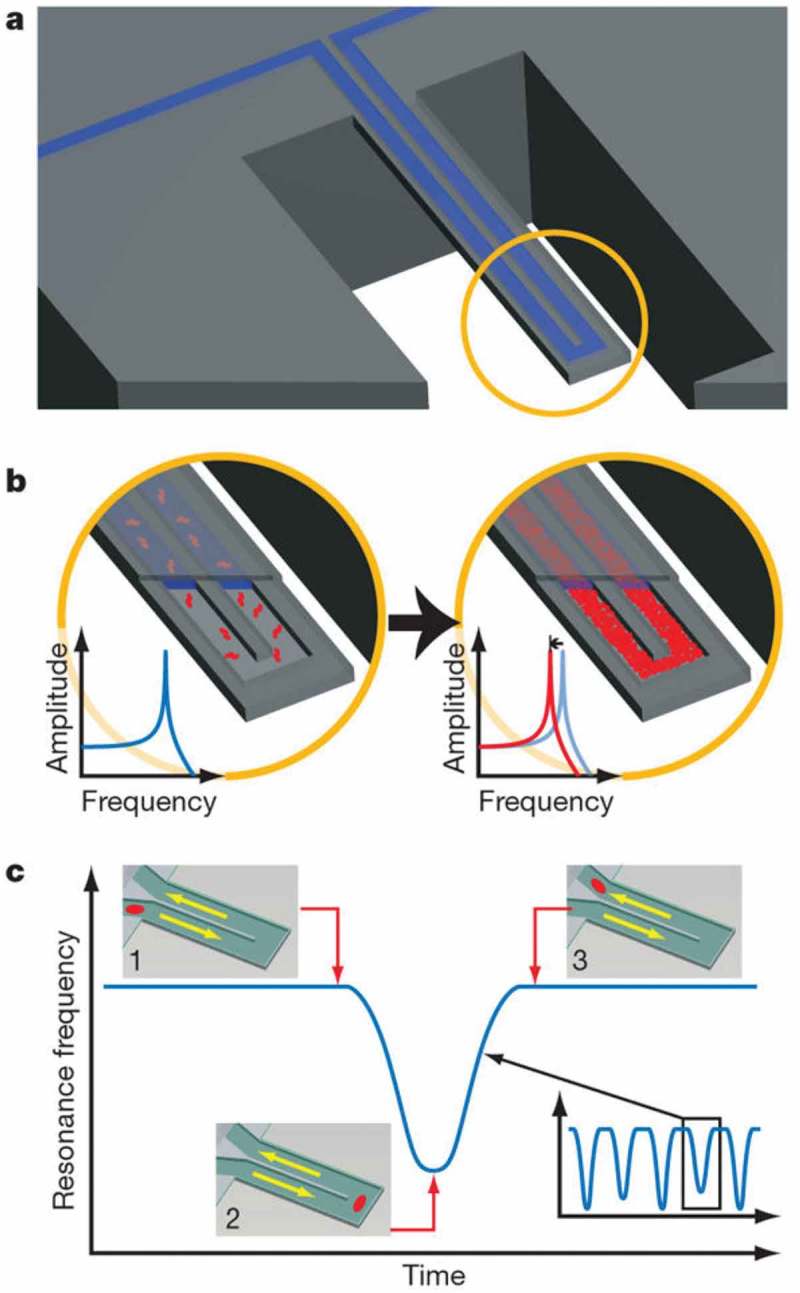
Schematic overview of resonant mass measurement, using systems such as Archimedes (Malvern Panalytical Ltd.). A suspended microchannel translates mass changes into changes in resonance frequency. Fluid continuously flows through the channel and delivers biomolecules, cells or synthetic particles (a). While bound and unbound molecules both increase the mass of the channel, species that bind to the channel wall accumulate inside the device, and, as a result, their number can greatly exceed the number of free molecules in solution. This enables specific detection by way of immobilised receptors (b). In another measurement mode, particles flow through the cantilever without binding to the surface, and the observed signal depends on the position of particles along the channel (insets 1–3). The exact mass excess of a particle can be quantified by the peak frequency shift induced at the apex (c). Reused with permission from Burg et al. [32].
