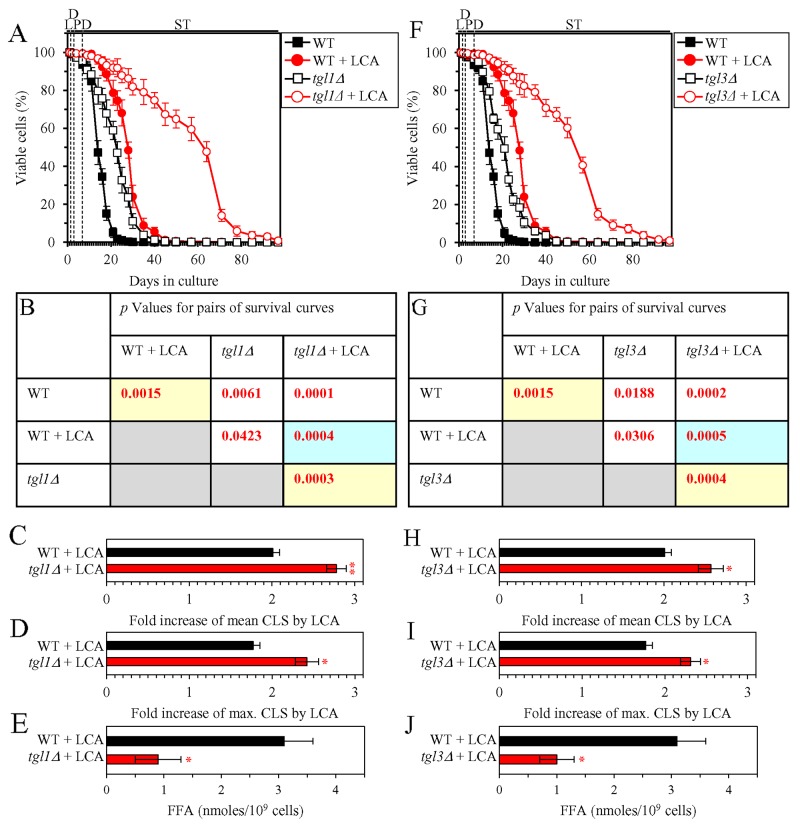
Figure 4. Under CR conditions in the presence of LCA, lack of the Tgl1 or Tgl3 enzymes involved in the TAG lipolysis that yields FFA decreases the concentration of FFA and increases the extent to which LCA can extend yeast CLS.
WT cells and mutant cells carrying a single-gene-deletion mutation eliminating either the Tgl1 or Tgl3 protein were cultured in the nutrient-rich YP medium initially containing 0.2% glucose with 50 μM LCA or without it. (A, F) Survival curves of the chronologically aging WT and tgl1Δ (A) or WT and tgl3Δ (F) strains are shown. Data are presented as means ± SEM (n = 3). Data for the WT strain cultured with or without LCA are replicated in graphs A, F of this Figure and in graphs A, F of Figure 5. (B, G) p Values for different pairs of survival curves of the WT and tgl1Δ (B) or WT and tgl3Δ (G) strains cultured with or without LCA. Survival curves shown in A or F (respectively) were compared. Two survival curves were considered statistically different if the p value was less than 0.05. The p values for comparing pairs of survival curves using the logrank test were calculated as described in Materials and Methods. The p values displayed on a yellow color background indicate that LCA extends the CLS of the WT (B and G), tgl1Δ (B) and tgl3Δ (G) strains. The p values displayed on a blue color background indicate that LCA extends the CLS of the tgl1Δ (B) and tgl3Δ (G) strains to a higher extent that that of the WT strain. (C, D, H, I) Survival curves shown in (A, F) were used to calculate the fold of increase of the mean (C, H) and maximum (D, I) CLS by LCA for the WT and tgl1Δ (C, D) or WT and tgl3Δ (H, I) strains. Data are presented as means ± SEM (n = 3; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01). (E, J) The maximum concentration of FFA, which was observed in WT and tgl1Δ (E) or WT and tgl3Δ (J) cells recovered on day 2 of culturing with LCA, is shown. Data are presented as means ± SEM (n = 3; *p < 0.05). Abbreviations: FFA, free fatty acids; L, D, PD and ST, logarithmic, diauxic, post-diauxic and stationary growth phases (respectively).