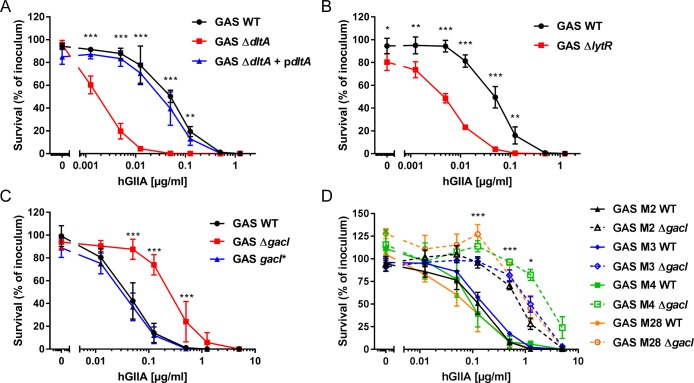
Fig 2. Mutation of dltA and lytR renders GAS more susceptible to hGIIA, whereas mutation of gacI increases hGIIA resistance in multiple GAS serotypes.
Deletion of (A) dltA or (B) lytR increases GAS susceptibility to hGIIA-mediated killing in a concentration-dependent manner. Deletion of gacI renders GAS more resistant to hGIIA-mediated killing as shown for (C) 5448 and (D) other tested GAS serotypes. Data represent mean +/- SD of three independent experiments. *, p ≤ 0.05; **, p ≤ 0.01; ***, p ≤ 0.001.