Figure 6.
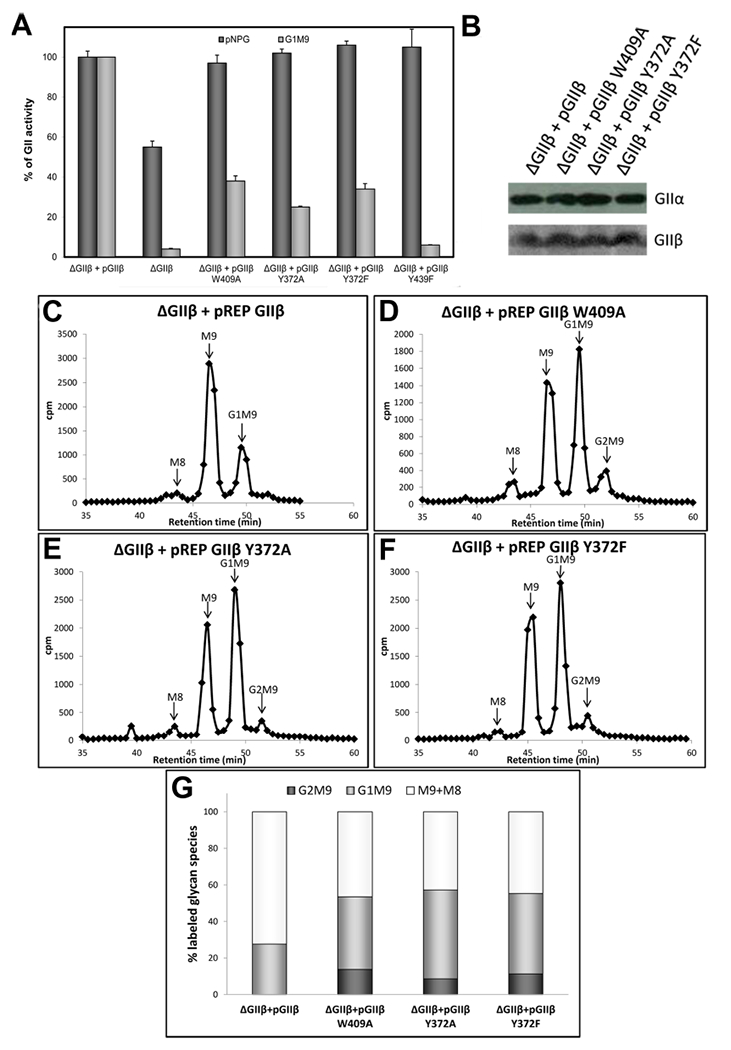
Influence of Y432 in GIIβ-mediated enhancement of GII activity toward N-glycans. (A) GII activity toward pNPG or Glc1Man9GlcNAc was measured using 125 μg of microsomes from S. pombe cells lacking endogenous GIIβ (ΔGIIβ) and expressing either GIIβ or the same subunit displaying the indicated mutations. The activity of ΔGIIβ cells transformed with wild-type GIIβ was taken as 100% for each substrate. Error bars represent the standard deviation. (B) Wild-type and mutant GIIβ expression levels and ER content of GIIα in the different S. pombe strains were evaluated by Western blotting. Microsomal proteins (125 μg) of S. pombe were resolved by 8% SDS-PAGE, transferred to a PVDF membrane, and blotted using rat polyclonal anti-GIIα (1:1000) or mouse polyclonal anti-GIIβ (1:5000). Goat antimouse IgG (1:5000) or goat antirat IgG (1:4000) conjugated to HRP were used as secondary antibodies. Reactions were detected by chemiluminescence. (C–F), glycan patterns synthesized in vivo by S. pombe ΔGIIβ mutant cells expressing GIIβ (C) or mutated GIIβ versions (D-F). Quantification of the relative amounts of the di-, mono-, and unglucosylated species from panels C–F is shown in panel (G). The label of Man8 species was added to that in Man9 species to account for unglucosylated glycans.
