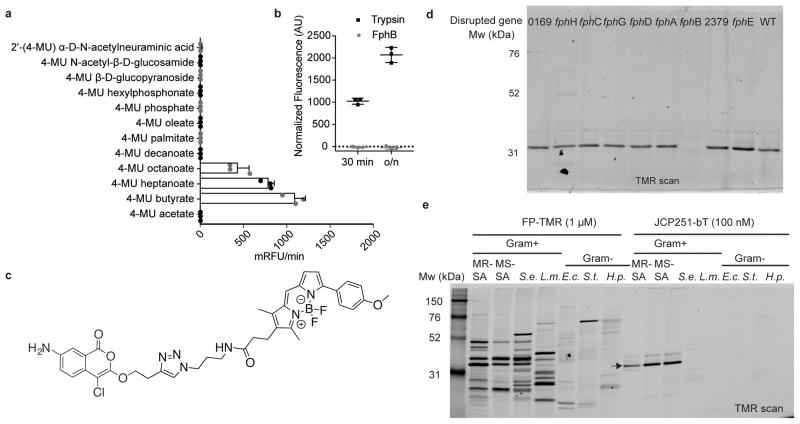
Fig. 3. Biochemical characterization of FphB and development of an FphB-selective fluorescent ABP.
a) Processing of 4-methylumbelliferyl-based fluorogenic substrates by rFphB. Turnover rates for each substrate are depicted as relative fluorescence units/min. Graph shows individual values overlaid with the means ± SD of 3 biologically independent samples. b) Proteolytic activity of rFphB or Trypsin against FITC-casein depicted as normalized fluorescence units. Graph shows an overlay of individual values and means ± SD, n= 3 biologically independent samples. Raw data were normalized by subtracting background fluorescence under buffer control conditions. c) Chemical structure of the fluorescent ABP JCP251-bT. d) SDS-PAGE analysis (TMR-fluorescence scan) of S. aureus Newman transposon mutant strains with insertions in indicated genes labeled with 100 nM JCP251-bT during exponential growth. (Full gel image in Fig. S4b) e) SDS-PAGE analysis of indicated Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial pathogens labeled with FP-TMR or JCP251-bT. MR-SA: S. aureus USA300, MS-SA: S. aureus ATCC35556, S.e.: S. epidermidis, L.m.: Listeria monocytogenes, E.c.: Escherichia coli, S.t.: Salmonella typhimurium, H.p.: Helicobacter pylori. Arrow indicates FphB. All experiments were repeated twice with similar results.