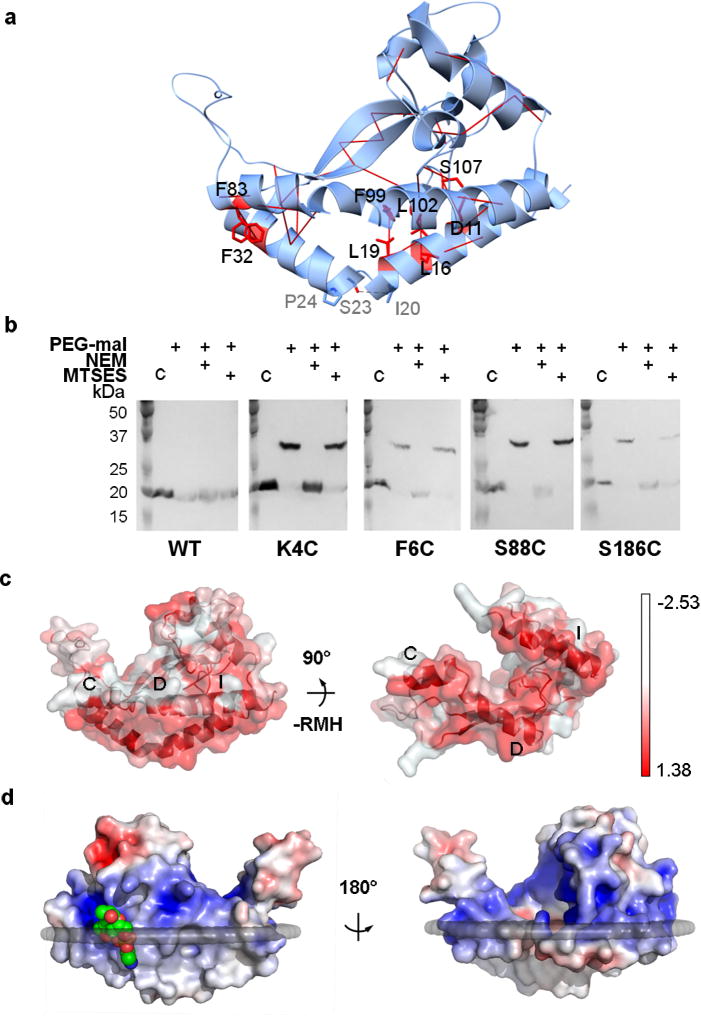
FIGURE 2. PglC crystallizes in a native conformation.
a, Co-evolution and covariance analyses across the monotopic PGT superfamily predict 10 interactions with ≥ 99% probability of contact (red solid lines). Phe32/Phe83 exhibit π-π-stacking; Leu19/Phe99, Leu16/Leu102, Thr29/Leu92, Tyr34/Val41, and Ala30/Val41 make hydrophobic interactions between the RMH and the coplanar helices; and Asp11/Ser107 form a hydrogen bond. b, In vivo SCAM analysis indicates that the N and C termini of PglC are localized on the cytoplasmic face (*, native PglC; **, PglC labeled with PEG-mal; C, control, no PEG-mal labeling). PEG-mal, PEG-maleimide; NEM, N-ethylmaleimide; MTSES, 2-sulfonatoethyl methanethiosulfonate. c, The hydrophobic surfaces (red) of amphipathic helices labeled C, D, and I establish a planar hydrophobic surface (left); also shown rotated 90° with RMH removed (right). d, A phosphatidylethanolamine (shown as space-filling, green) head group binding site at Arg8 locates this position to the membrane interface. The surface is colored by electrostatic potential from +5 kT/e (blue) to −5 kT/e (red).