Figure 7. Transfection of mitochondria-targeted OGG1 (Mt-OGG1) or SOD2 eliminated preexisting mtDNA4977 deletion mutation and improved mitochondrial function.
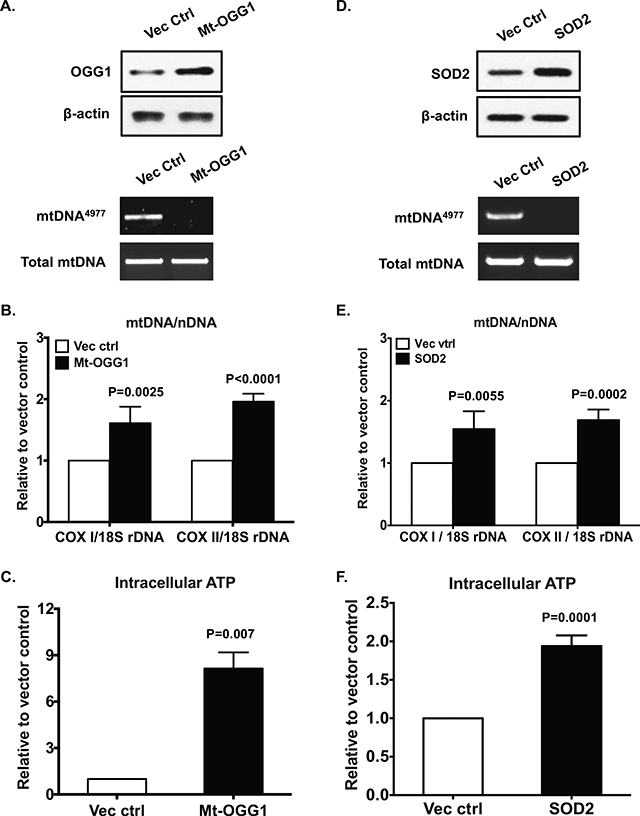
Primary human knee OA chondrocytes were transfected with pCMV/myc/mito-hOGGl or pBI-EGFP-MnSOD and the vector controls for 48 hours. Expression of OGG1 and SOD2 were examined by Western blot (A and D, top panel). The mtDNA4977 deletion mutation (A and D, bottom panel), mtDNA content (B and E) and intracellular ATP (C and F) were assayed as above. Data in A and D represent 3 individual experiments with 3 different OA donors (1 male and 2 females, age 68, 78 and 57, respectively). Data in B, C, E and F were the mean of 3 individual experiments with 3 different OA donors (the same donors as in A, n=3 with 3–4 replicates for each donor). Student t-test was used for statistical data analysis in B and C comparing the vector control with Mt-OGG1, and in E and F comparing the vector control with SOD2. The mean differences, 95% CIs and p values for COXI/18S rDNA and COXII/18S rDNA were 0.61±0.11, 0.37 to 0.85, p=0.0002 and 0.96±0.05, 0.84 to 1.08, p<0.0001 in B, and 0.54±0.12, 0.28 to 0.8, p=0.0009 and 0.69±0.07, 0.53 to 0.84, p<0.0001 in E. The mean differences, 95% CIs and p values for ATP levels were 7.14±0.6, 5.48 to 8.8, p=0.0003 in C and 0.94±0.06, 0.79 to 1.08, p<0.0001 in F.
