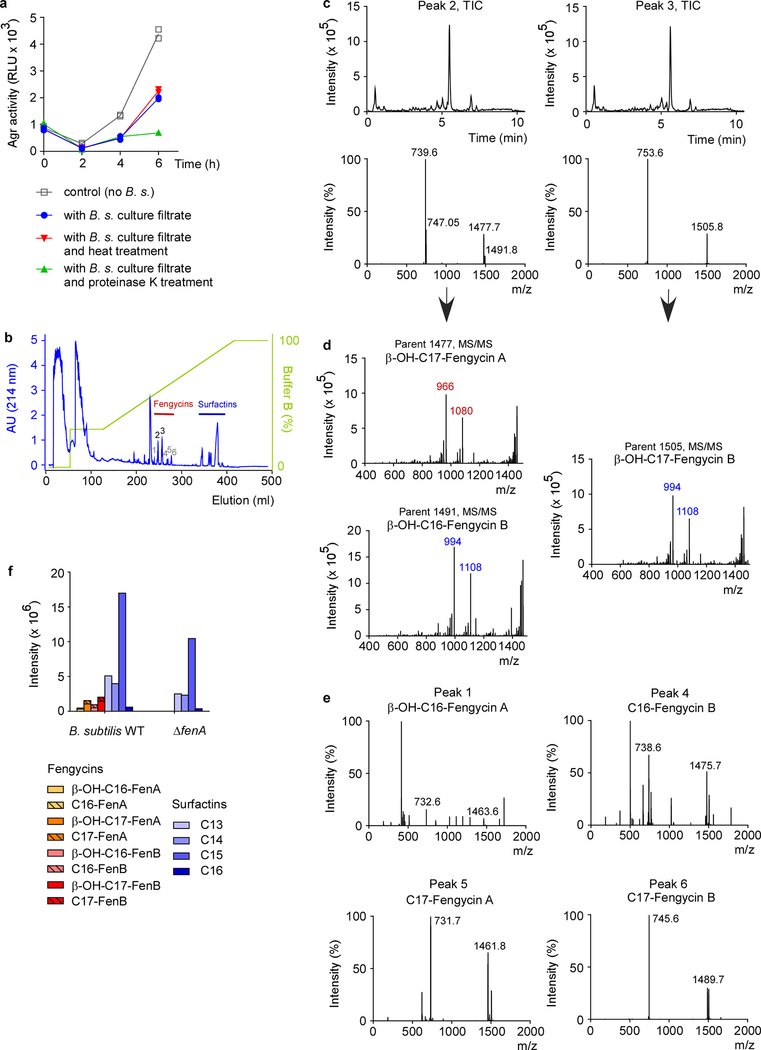
Extended Data Figure 3 |. Analysis of Agr-inhibitory substances.
a, Influence of heat and protease on Agr inhibition. B. subtilis (B. s.) culture filtrate was subjected to heat (95 °C, 20 min) or proteinase K digestion (50 μg/ml, 37 °C, 1 h) and the impact on inhibition of Agr activity was measured using the luminescence assay with the USA300 P3-luxABCDE reporter strain (see Fig. 3a). RLU, relative light units. The experiment was performed with n=2 independent biological samples. Lines connect the means. (The observed additional suppression of Agr activity in the proteinase K-treated sample at 6 h, as compared to the B.s. culture filtrate sample, is expected due to proteolytic inactivation of intrinsic AIP.) b, Preparative RP chromatography of B. subtilis culture filtrate to determine the Agr-inhibiting substance. The peaks labeled 2 and 3 showed significant Agr-inhibiting activities in the Agr activity assay and were identified as fengycins using subsequent RP-HPLC/ESI-MS and MS/MS analysis (see c,d). The peaks labeled 1 and 4–6 also contained fengycin species (see e). c, Fractions corresponding to the Agr-inhibitory peaks 2 and 3 from the preparative RP run (b) were subjected to RP-HPLC/ESI-MS. Top, total ion chromatograms (TICs) of the RP-HPLC/ESI-MS runs; bottom, ESI mass spectrogram of the major peaks. d, MS/MS analysis of the peak 2 and 3 fractions. Peaks that are characteristic for a given fengycin subtype (A or B in this case) are marked in color. e, Analysis of further fengycin-containing fractions. Peaks 1, 4, 5, and 6 from the preparative RP run (b) were also found to contain fengycin species as determined by subsequent RP-HPLC/ESI-MS analysis. Shown are the mass spectrograms of the major peaks of those runs and the tentative characterization for fengycin type. The preparative and analytical chromatography and HPLC/MS analyses (as shown in b and d) were repeated multiple (> 10) times for fengycin purification with similar results. MS/MS analyses were not repeated. f, Analysis of fengycin and surfactin lipopeptide expression of the B. subtilis wild-type strain and its isogenic ΔfenA mutant.