Figure 5.
The Duplex Interaction Surface Contributes to RNA Binding and Cleavage
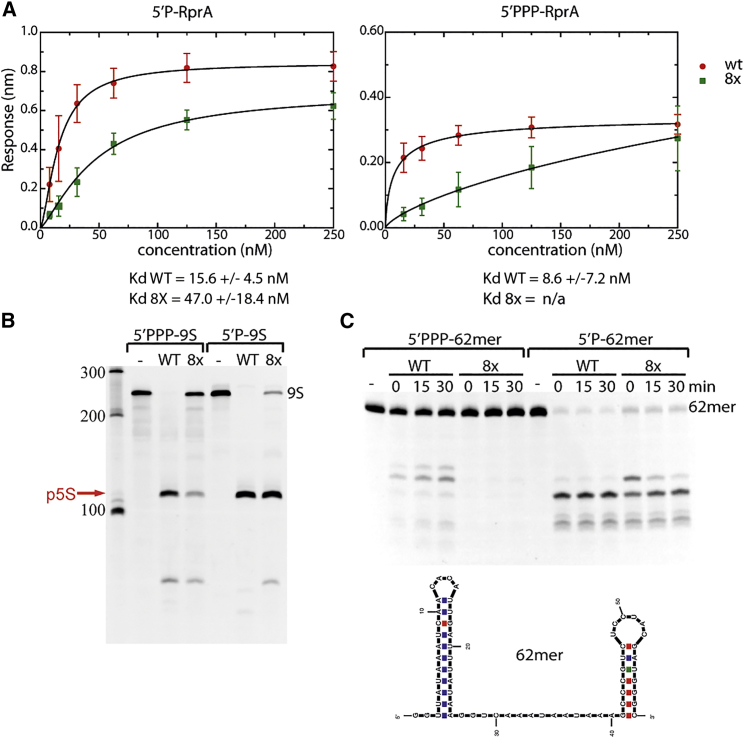
(A) 5′ mono- and triphosphorylated RNA binding by RNaseE (1–529) wild-type (WT) and duplex binding site mutant (8x). The binding experiments were done under conditions in which cleavage is not occurring. The mutant binds 5′ monophosphorylated RprA with about a third the affinity seen for the WT enzyme, but the affinity for triphosphorylated substrate is substantially reduced. The profiles show averages and SDs from three technical replicates.
(B) 9s rRNA (200 nM) with 5′ tri- or monophosphate processing by 1 μM RNaseE (1–529) WT and 8x mutant.
(C) 62-mer RNA (5 μM) with 5′ tri- or monophosphate processing by 1 μM RNaseE (1–529) WT and 8x mutant.