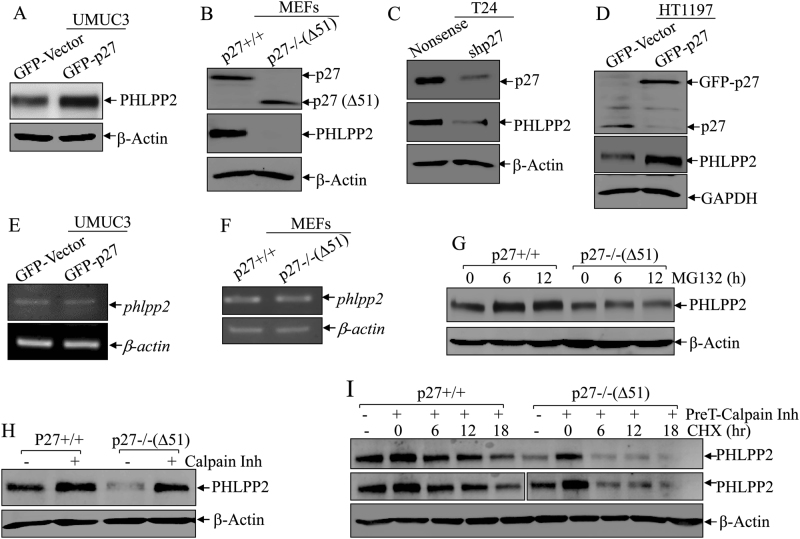
Fig. 2.
PHLPP2 was regulated by p27 at protein degradation level in Calpain-associated mechanism. a–d Western blot (WB) was used to detect the protein levels of PHLPP2 in UMUC3(Vector) vs UMUC3(GFP-p27) cells (a), p27+/+ vs p27−/−(Δ51) (b), T24(Nonsense) vs T24(shp27) (c), HT1197(Vector) vs HT1197(GFP-p27) (d). β-Actin or GAPDH was used as protein loading control. e, f RT-PCR was applied to compare the mRNA levels of phlpp2 in UMUC3(Vector) and UMUC3(GFP-p27) cells (e), and p27+/+ vs. p27−/−(Δ51) (f). β-actin was used as internal control. g p27+/+ and p27−/−(Δ51) cells were treated with MG132 for the indicated times. The cell extracts were then subjected to western blot to analyze PHLPP2 protein accumulation among the indicated cells. β-Actin was used as protein loading control. h p27+/+ and p27−/−(Δ51) cells were treated with Calpain inhibitor for 12 h. The cell extracts were then subjected to western blot analyses of PHLPP1 protein accumulation among the indicated cells. β-Actin was used as protein loading control. i p27+/+ and p27−/−(Δ51) cells were pre-treated with Calpain inhibitor for 12 h and the treated cells were subjected to protein degradation assay in presence of CHX and absence of Calpain inhibitor for the indicated time points. The cell extracts were then subjected to Western Blot to analyze PHLPP2 protein degradation rates between the indicated cells. β-Actin was used as protein loading control