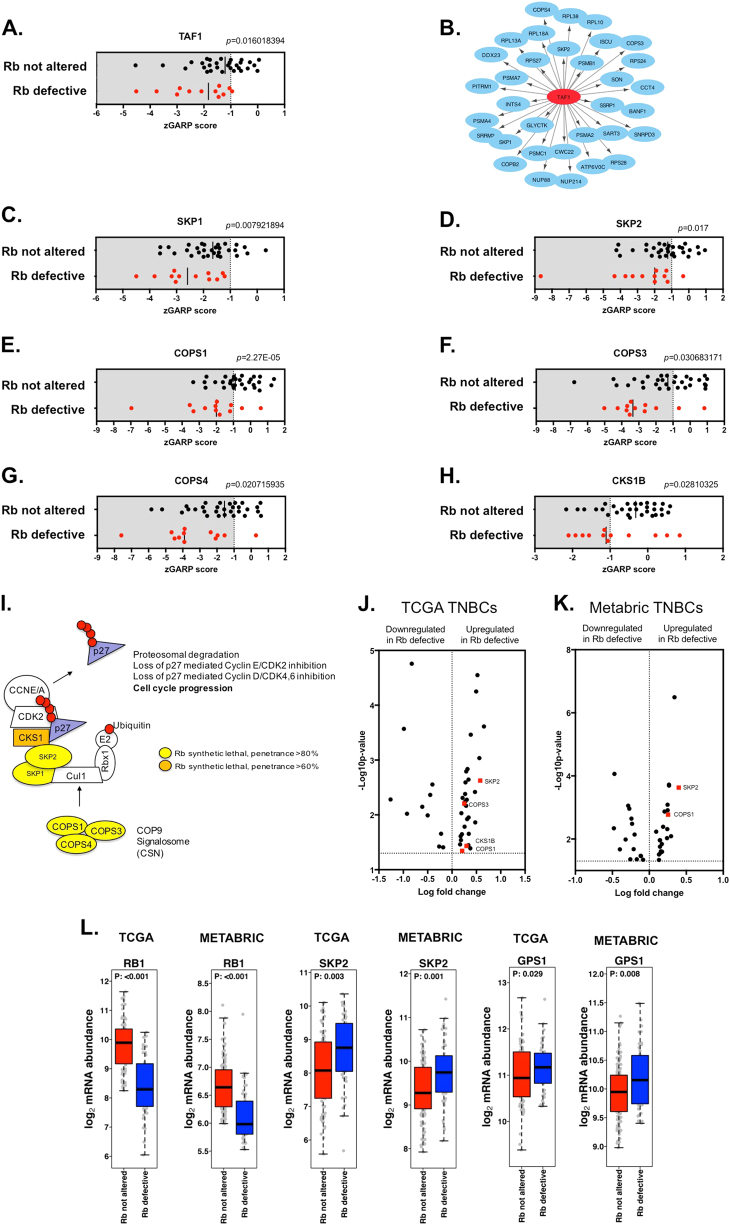
Fig. 4.
TAF1 and SKP2 as central nodes in highly penetrant Rb synthetic lethal networks. a Scatter plot illustrating Z scores in 42 TNBC TCLs for TAF1 from the data analysis illustrated in Fig. 2a. b Cytoscape network plot illustrating 33 highly penetrant (>80% penetrance) Rb synthetic lethal effects identified as TAF1 transcription factor target genes, as annotated by ENCODE data [26, 44]. c–h Scatter plots illustrating Z scores in 42 TNBC TCLs for SKP1, SKP2, COPS1,3,4 and CKS1B from the data analysis in Fig. 2a. i Pathway diagram highlighting the role of multiple highly penetrant Rb synthetic lethal effects in the control of p27 activity. j Volcano plot illustrating mRNAs from highly penetrant Rb SL genes that are differentially expressed (limma analysis p < 0.05) in 48 Rb-defective vs. 92 Rb not altered triple-negative breast tumours from the TCGA study [27]. Four highly SCFSKP/COP9 complex genes, highlighted in red, demonstrate significantly higher mRNA expression levels in the Rb-defective cell lines. k As per j, using data from the Metabric study [28]. l Box plots illustrating elevated SKP2 or GPS1 (COPS1) mRNA expression in Rb-defective TNBC from both the TCGA [27] and Metabric studies [28]. p-values shown calculated with Wilcox rank sum test