Fig. 6.
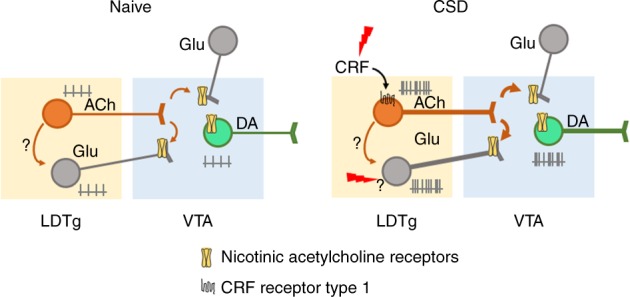
Schematic model of the findings. In naive conditions, LDTg excitatory projections regulate the firing and bursting activity of VTA DA neurons. Chronic social defeat (CSD) increases the excitability of LDTg cholinergic and glutamatergic neurons that project to the VTA. Enhanced acetylcholine release increases VTA DA firing via direct activation of neuronal acetylcholine nicotinic receptors, but also by enhancing glutamatergic release via presynaptic modulation. CRF binds to CRF-1 receptors in cholinergic but not glutamatergic neurons, to promote firing in response to stress. The mechanisms by which LDTg glutamatergic neurons increase excitability after CSD are not clear, but may involve local cholinergic innervation, direct stress-related signaling, or others inputs to LDTg glutamatergic neurons
