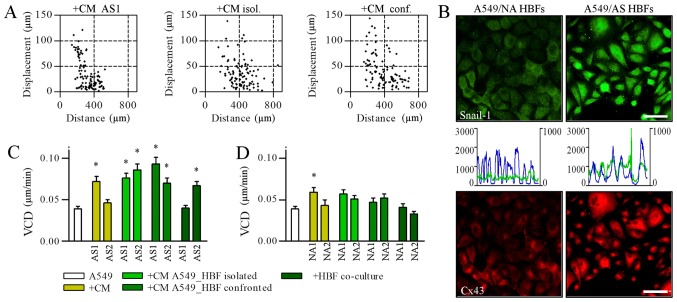
Figure 2.
AS HBFs induce the motility of A549 cells via contact-modulated paracrine signaling. (A) A549 cells were cultivated in the media conditioned by AS2 HBFs (left), ‘separated’ (middle) and ‘confronted’ AS HBF/A549 co-cultures (1:1 v/v with fresh medium) for 48 h and (C) the parameters of their motility were analyzed by time-lapse videomicroscopy in comparison to A549 motility in control conditions and in ‘open’ AS HBF/A549 co-cultures. (B) A549 cells were cultivated in the media conditioned by ‘separated’ co-cultures of A549 with AS and NA HBFs (1:1 v/v with fresh medium) for 48 h. Intracellular localization of Snail-1/Cx43 and co-localization of Snail-1/DNA was visualized with immunofluorescence and cytofluorimetry, respectively (left axes/blue line: DNA; right axes/green line: Snail-1). Scale bar, 50 µm; magnification, ×400. (D) The motility of A549 cells in the presence of the media conditioned by NA HBFs (left), ‘separated’ (middle) and ‘confronted’ NA HBF/A549 co-cultures (1:1 v/v with fresh medium) was analyzed as in (A). Data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean of 3 independent experiments. *P<0.05 vs. A549. Note the mobilization of A549 in the presence of AS HBF/A549-conditioned media, which was correlated with Snail-1/Cx43 activation. HBFs, human bronchial fibroblasts; AS, asthmatic donors; NA, non-asthmatic donors; VCD, velocity of cell displacement; Cx43, connexin43; CM, conditional media.