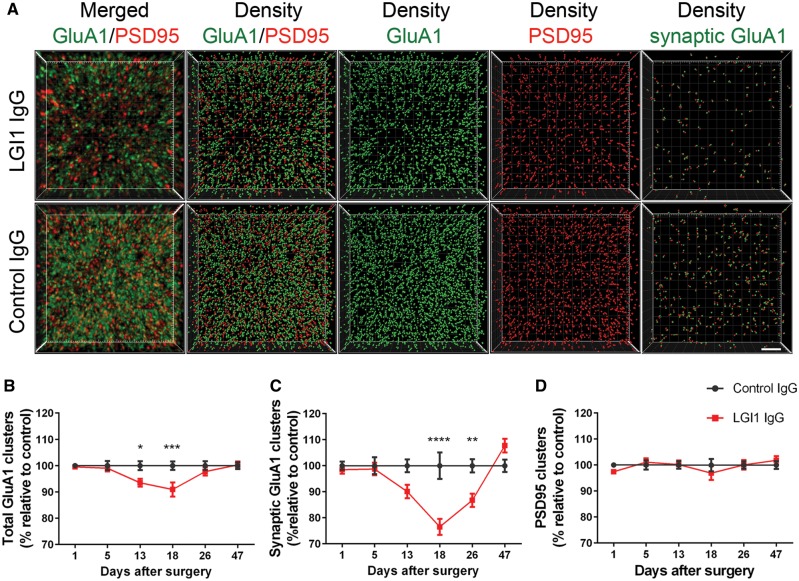
Figure 4.
Patient-derived LG1 IgG causes a decrease of total cell surface and synaptic AMPAR clusters in the hippocampus. (A) 3D projection and analysis of the density of total clusters of GluA1 AMPAR and PSD95, and synaptic clusters of AMPAR (defined as AMPAR clusters that co-localized with PSD95) in one of the CA3 subregions indicated in Fig. 3A, ‘Analysis’. Merged images (A, top and bottom left; GluA1 green, and PSD95 red) were post-processed and used to calculate the density of the indicated clusters (density = spots/μm3). Scale bar = 2 μm. (B–D) Quantification of the density of total (B) and synaptic (C) GluA1 AMPAR clusters, and PSD95 clusters (D) in a pooled analysis of hippocampal subregions (CA1, CA3, dentate gyrus) in animals treated with patient-derived LGI1 IgG (red) or control IgG (black) on the indicated days. Mean density of clusters in control IgG treated animals was defined as 100%. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. For each time point five animals infused with patient-derived IgG and five with control IgG were examined. Significance of treatment effect was assessed by two-way ANOVA with an alpha-error of 0.05 (asterisks) and post hoc testing with Sidak-Holm adjustment. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.