Figure 2.
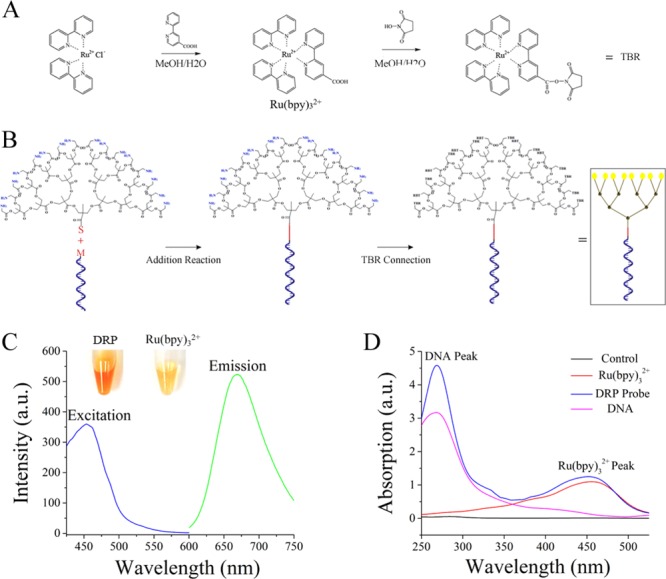
Synthetic routes for Ru(bpy)32+ and the dendritic Ru(bpy)32+-polymer. (A) Synthetic route and activation process of Ru(bpy)32+. The concentration of MeOH was 80%. The details of the crystallization, separation, and purification processes are provided in section 1.1 of the Supporting Information. (B) Synthetic route for the dendritic Ru(bpy)32+-polymer probe. The DNA recognition domain was labeled with maleimide, abbreviated as M. The dendritic polymer was labeled with amino and sulfhydryl group. Sulfhydryl, abbreviated as S, could bond with maleimide via an addition reaction. The amino group provided the conjugation site for Ru(bpy)32+. The details of the purification process and the complete structure of the dendritic Ru(bpy)32+-polymer are shown in section 1.1 of the Supporting Information. (C) Excitation and emission of the dendritic Ru(bpy)32+-polymer. The concentrations of the solutions were identical. DRP represents the dendritic Ru(bpy)32+-polymer. The excitation peak of the dendritic Ru(bpy)32+-polymer was at 450 nm, and the emission peak was at 660 nm. (D) Absorption spectrum of the dendritic Ru(bpy)32+-polymer-amplified ECL probe. Absorption peaks simultaneously appeared at 260 and 450 nm after the dendritic Ru(bpy)32+-polymer was linked with nucleic acids.
