Figure 3.
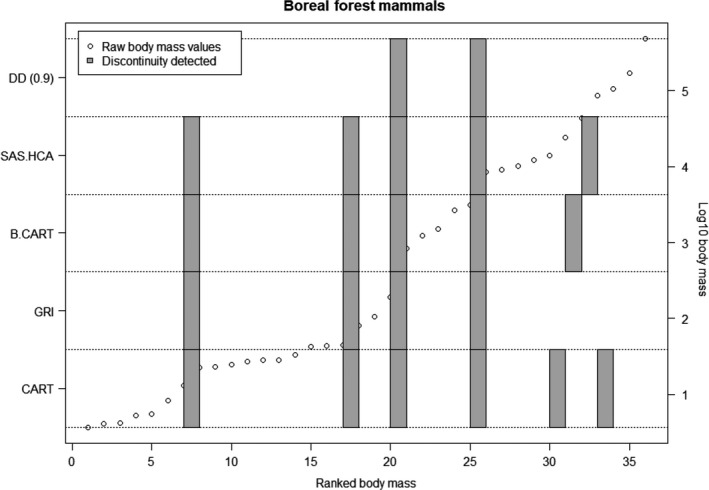
A comparison of the discontinuity detector versus the other methods. The hollow circles represent the raw body mass data (log 10 scale, on right‐hand axis.) against the rank body size (x‐axis). The gray squares represent where a discontinuity has been identified, by each of the different methods. Each method is stacked on top of each other to show which rank the discontinuity has been detected (y‐axis—left‐hand side). We compare hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA), Bayesian classification and regression trees (BCART), classification and regression trees (CART), and Gap Rarity Index (GRI). The (0.9) represents the acceptance value used to accept the discontinuity, that is, the observed data are >90% percentile of the bootstrap comparison. Here, we present the Boral forest mammal dataset of Holling (1992), in Figure 4, we show the results, presented similarly, of the comparisons for other datasets
