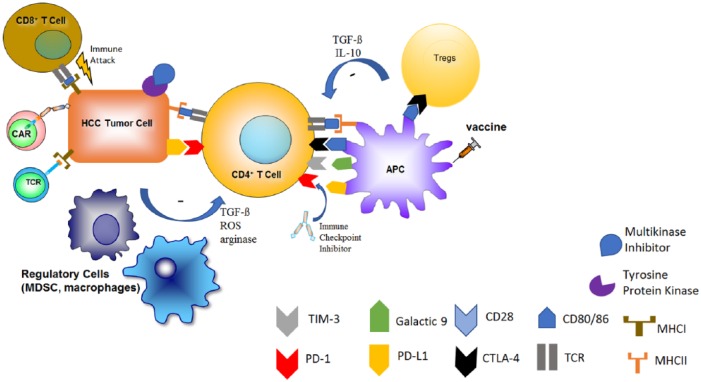
Figure 1.
Current landscape of systemic HCC therapy.
The mainstay of treatment for advanced HCC over the past decade has been the multikinase inhibitor, sorafenib. Within the last few years, more of these multikinase inhibitors have been found to have success in treating HCC. Unlike typical chemotherapy, immunotherapies rely on activating a person’s own immune system or the transfer of immune cells to elicit tumor eradication. The tumor microenvironment may create an immunosuppressive milieu through recruitment of Tregs, MDSCs, and upregulation of immune checkpoints. These immunosuppressive factors lead toward carcinogenesis and tumor progression. Therapies such as immune checkpoint inhibitors, cancer vaccines, cytokine-based therapies, and adoptive cell transfer have attempted to promote antigen recognition and subsequent tumor eradication.
HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; MDSC, myeloid-derived suppressor cell; Treg, regulatory T-cell.