Figure 3.
EVs Released from Morphine-Exposed Astrocytes Induce Nuclear Translocation of NF-κB
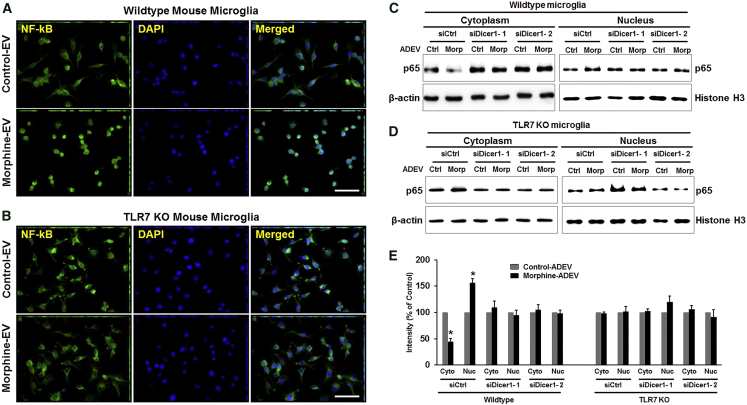
(A and B) Wild-type (A) and TLR7 KO (B) mouse primary microglial cells were treated with EVs (2 μg of EVs per 2 × 105 cells) isolated from morphine-exposed astrocytes for 30 min. The subcellular localization of endogenous p65 was visualized by indirect immunofluorescence using anti-p65 antibodies (green). Nuclear DNA was revealed by DAPI staining. Scale bars, 50 μm. (C and D) Primary mouse astrocytes were transfected with either control or Dicer-siRNA for 24 hr, followed by morphine exposure for 24 hr. Wild-type (C) and TLR7 KO (D) mouse microglial cells were exposed to EVs (30 min) isolated from astrocyte conditioned media followed by detection of NF-κB p65 in the nuclear fraction by western blot. (E) All experiments were done at least three independent times. Band intensities of the cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts were quantified and normalized against β-actin and histone H3, respectively, and compared with untreated cells. All data are presented as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05 versus control using Student’s t test.