Fig. 2.
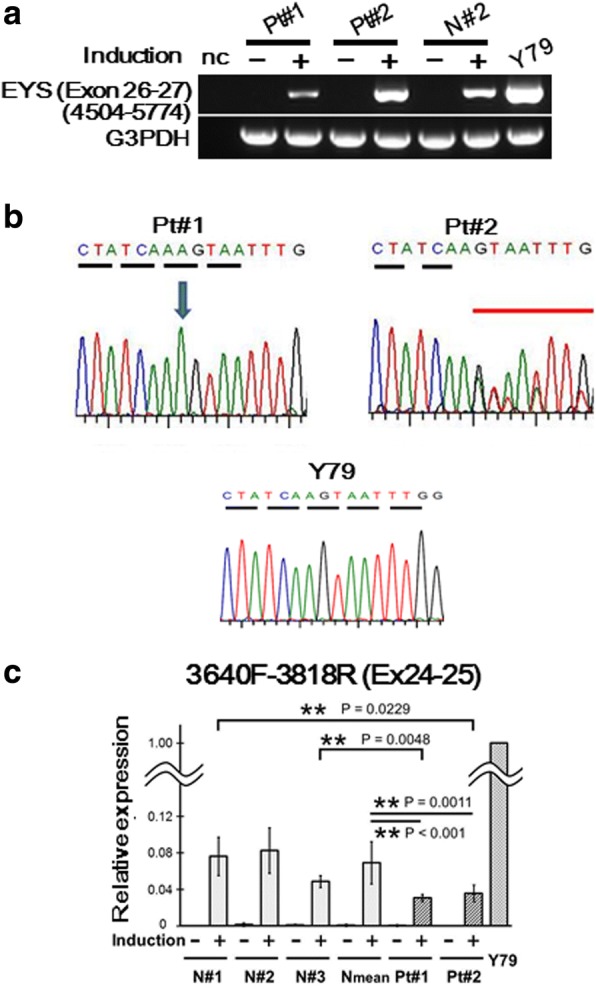
Detection of expression and identification of sequences of EYS transcripts corresponding to exon 26–27 that includes c.4957dupA in photoreceptor-directed fibroblasts from EYS-RP patients. a RT-PCR analysis of expression of EYS gene using primer pairs corresponding to exon 26–27. Expression levels of EYS gene were clearly up-regulated by CRX, RAX, NeuroD and OTX2 transduction in Pt#1, Pt#2 and N#2 10 days after transduction. Y79 was used as a positive control. b Electropherogram corresponding to c.4957dupA by sequencing of RT-PCR products. The transcripts had c.4957dupA mutation in photoreceptor-directed fibroblasts from Pt#1carrying homozygous mutation and Pt#2 carrying compound heterozygous mutation. As for Pt#2, the peak amplitudes of mutated bases on the electropherogram seemed to be lower than normal bases. c Analysis of expression levels of EYS gene corresponding to exon 24–25 by qRT-PCR. Vertical axis indicates relative expression (mean ± SD, n = 4 for Pt#1 and Pt#2, n = 3 for N#1, N#2 and N#3). To compare expression levels of defected EYS gene transcripts (Pt#1 and Pt#2) to normal (N#1, N#2, N#3), we performed qRT-PCR for photoreceptor-directed fibroblasts 10 days after transduction. We designed primer pairs nearly upstream to c.4957dupA (exon 24–25, 3640F-3818R) and compared the expression levels of EYS gene corresponding to exon 24–25. Expression levels of exon 24–25 were significantly lower in Pt#1 (Wilcoxon test, p < 0.001) and Pt#2 (P = 0.0011) compared to the average of three normal volunteers. Those of Pt#1 was also lower than age-matched control, N#3 ((Wilcoxon test, p < 0.001)
