Fig. 5.
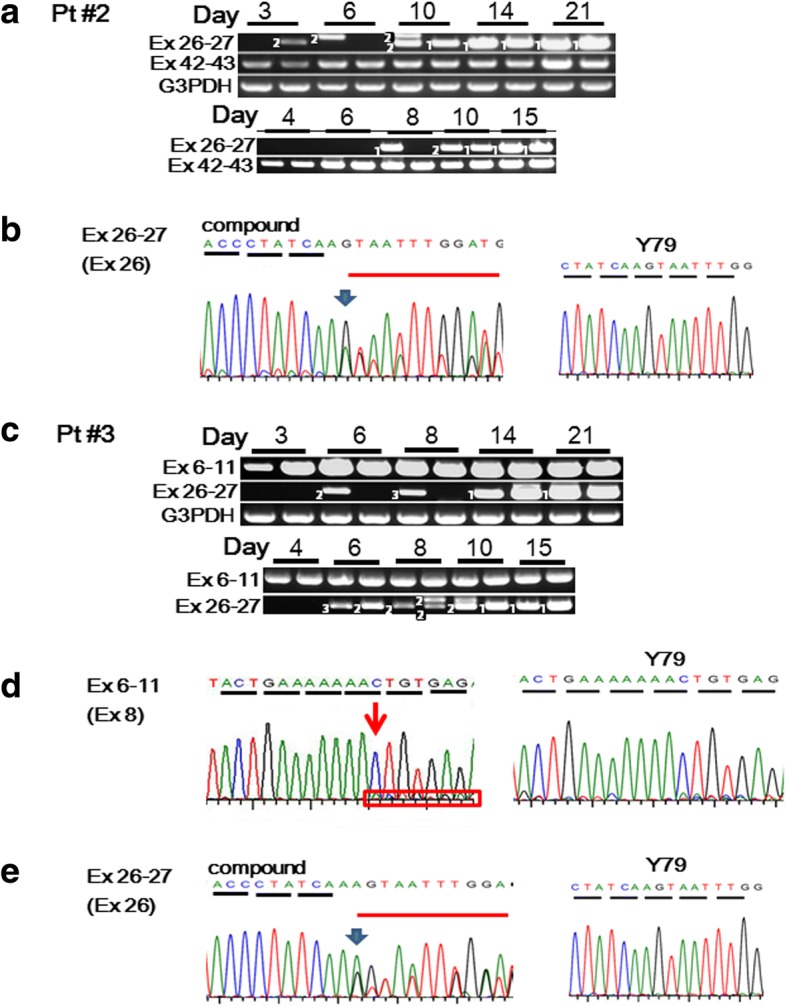
Changes of compositions of EYS gene transcripts over time during photoreceptor-directed differentiation. a Changes of compositions of EYS gene transcripts of Pt#2 by endpoint RT-PCR and sequencing. b Representative patterns of electropherogram corresponding to exon 26–27 including c.4957dupA. Endpoint RT-PCR products amplified for exon 26–27 and exon 42–43 at 3, 4, 6, 8, 10, 14, 15 and 21 days during photoreceptor-directed differentiation for Pt#2 (a). Two independent induction-experiments were performed for 3–21 days and for 4–15 days. In each time-course experiment, induction was performed in duplicate and endpoint RT-PCR was performed using each induced sample. Sequencing analyses revealed that these RT-PCR products corresponding to exon 26–27 derived from Pt#2 consisted of either compound transcripts of normal and mutated sequences (1) or only mutated sequence (2) at some time points before 14 days. After 14 days, amplified fragments contained compound transcripts of normal and mutated sequences. Representative electropherogram of “compound” pattern shown in panel b indicates the peak amplitudes of mutated bases were lower than normal bases. Sequences of RT-PCR products corresponding to exon 42–43 for Pt#2 showed compound transcripts of normal and mutated sequences at all the time points during induction. Endpoint RT-PCR products corresponding to exon 26–27 including c.4957dupA, yielded products with different mobility before 10 days (a). Sequencing the PCR products verified that these were alternatively spliced EYS gene transcripts (Additional file 1: Figure S6). c Changes of compositions of EYS gene transcripts of Pt#3 by endpoint RT-PCR and sequencing. d, e Representative patterns of electropherogram corresponding to exon 6–11 including c.1211dupA (d) and corresponding to exon 26–27 including c.4957dupA (e). Endpoint RT-PCR products amplified for exon 6-11and exon 26–27 at 3, 4, 6, 8, 10, 14, 15 and 21 days during photoreceptor-directed differentiation for Pt#3 (c). Two independent induction-experiments were performed for 3–21 days and for 4–15 days. In each time-course experiment, induction was performed in duplicate and endpoint RT-PCR was performed using each induced sample. Sequencing analyses revealed that these RT-PCR products corresponding to exon 6–11 consisted of normal sequences with a very low level of defected sequences (d). Sequencing analyses revealed that these RT-PCR products corresponding to exon 26–27 consisted of either compound transcripts of normal and mutated sequences ((1), “compound” (e)), only mutated sequence (2) or only normal sequence (3) at some time points before 14 days. However, after 14 days, amplified fragments contained compound transcripts of normal and mutated sequences. The electropherogram (e) indicates the peak amplitudes of normal bases were lower than mutated bases
