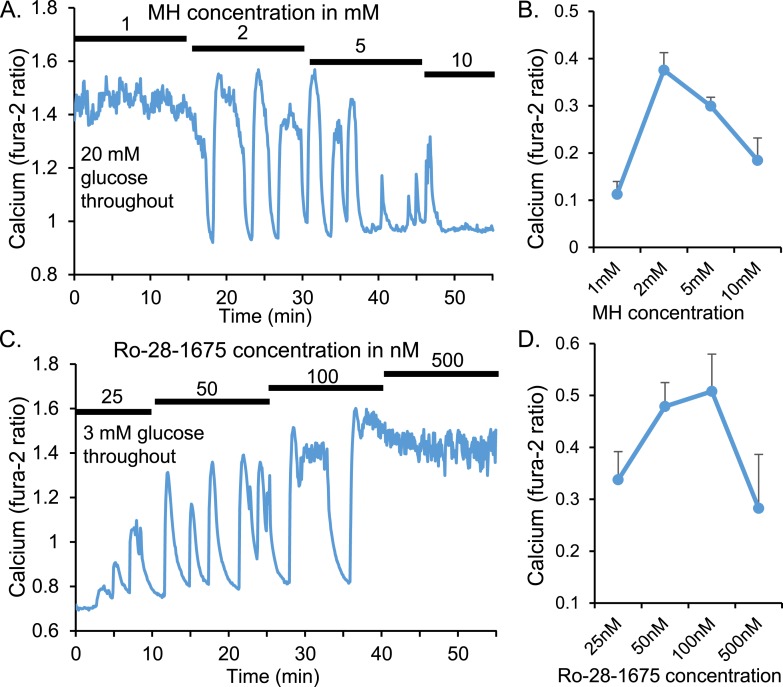
Figure 2.
Islet pulsatility depends on glucokinase activity. (A) Representative [Ca2+]i trace showing increasing doses of the glucokinase inhibitor MH in high (20 mM) glucose causes constitutively high [Ca2+]i to go through a range of pulsatile patterns to basal [Ca2+]i. (B) Mean amplitude ± SEM of [Ca2+]i oscillations for each MH concentration (n = 12 islets). (C) Stimulation of glucokinase activity by Ro-28-1675 led to a dose-dependent increase in [Ca2+]i pulsatility to constitutive calcium influx at the highest Ro-28-1675 concentration (n = 12 islets). (D) Mean amplitude ± SEM of [Ca2+]i oscillations for each Ro-28-1675 concentration.