FIGURE 7.
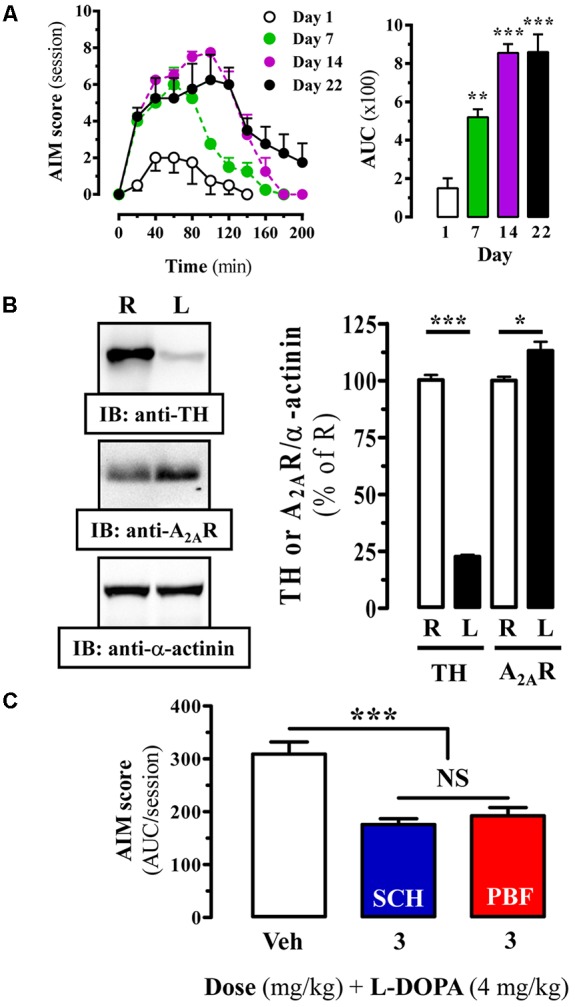
Effect of PBF509 in LID rats. (A) L-DOPA induced-motor side effects (i.e., LIDs) development upon chronic (22 days) L-DOPA (4 mg/kg) administration. AIM score was measured during a 220-min on days 1, 7, 14, and 22 after the corresponding daily L-DOPA administration. The total AIMs score over 200 min was quantified and expressed as area under the curve (AUC) ± SEM (n = 8). ∗∗P < 0.01 and ∗∗∗P < 0.001 one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test when compared to day 1. (B) Immunoreactivity of A2AR in the striatum of dyskinetic rats. TH and A2AR density in striatal membranes from control (R) and 6-OHDA lesioned (L) striatal hemisphere of LID animals was analyzed by immunoblot and quantified as described in Figure 4. Data are expressed as percentage of the control (R) TH or A2AR density ± SEM of three independent experiments. Asterisks indicate data significantly different from the control condition: ∗∗∗P < 0.001, ∗P < 0.05 by Student’s t-test. (C) LID attenuation in chronic (22 days) L-DOPA (4 mg/kg) administered rats following administration of A2AR antagonists. The total AIM score (area under the curve, AUC) obtained over 220 min following co-administration of L-DOPA (4 mg/kg) plus vehicle (Veh), SCH420814 (3 mg/kg) and PBF509 (3 mg/kg) are presented as mean score ± SEM (n = 6). The asterisks denote data significantly different from the vehicle condition: ∗∗∗P < 0.001, one-way ANOVA with a Bonferroni’s post hoc test. NS: not statistically significant.
