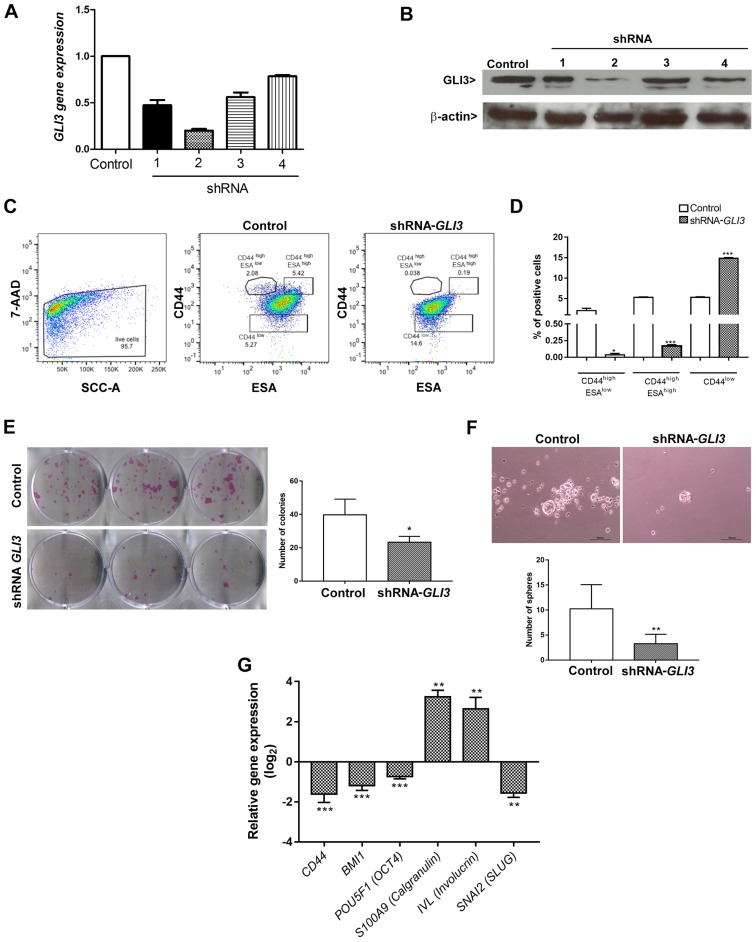
Figure 4.
Effects of GLI3 knockdown on SCC9 stemness. (A) GLI3 mRNA expression levels and (B) GLI3 protein expression in SCC9 cells transfected with control or shRNA-GLI3. (C) FACS analysis of the expression of CD44 (y-axis) and ESA (x-axis) on control and shRNA GLI3 SCC9 cells. GLI3 knockdown decreases CD44high/ESAlow and CD44high/ESAhigh fractions of SCC9 cells, as well as increased the CD44low fraction. (D) Quantification of data depicted in (C), showing the percentage of CD44high/ESAlow, CD44high/ESAhigh and CD44low fractions. (E) Colony formation ability and quantification of the number of colonies formed in shRNA GLI3 and control cells. (F) Number of spheres formed in shRNA GLI3 and control cells. (G) RT-qPCR indicated reduced CD44, BMI1, POU5F1 (OCT4) and SNAI2 (SLUG) mRNA expression and increased S100A9 (Calgranulin) and Involucrin (IVL) in shRNA-GLI3-transfected cells in relation to the control cells. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 (t-tests with the Welch correction). Microscope images: Magnification, ×100 (scale bars, 40 μm).