Figure 5.
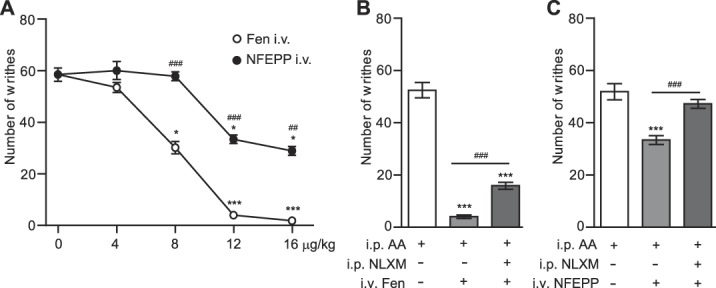
Contribution of peripheral opioid receptors to analgesic effects of intravenous (i.v.) fentanyl and NFEPP in the abdominal pain model. (A) Dose-dependent analgesic effects of i.v. fentanyl (Fen) and NFEPP. Agonists were injected immediately after 1% acetic acid (i.p.) and the total number of writhes was counted at 5 to 35 minutes thereafter. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.01 vs control (0 µg/kg), Kruskal–Wallis 1-way ANOVA and Dunn test; ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001, NFEPP vs Fen, Mann–Whitney test. (B and C) Effects of NLXM (50 μg i.p.) on analgesia induced by Fen (B) and NFEPP (C) (both at 12 µg/kg i.v.). NLXM was injected i.p. immediately after acetic acid (AA) injection and right before i.v. injections of agonists, and the total number of writhes was counted at 5 to 35 minutes thereafter. ***P < 0.001 vs control groups receiving acetic acid and vehicle (white bars); ###P < 0.001, 1-way ANOVA and Bonferroni test. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM; n = 9 rats per group. ANOVA, analysis of variance; i.p.,intraperitoneal.
