Figure 2.
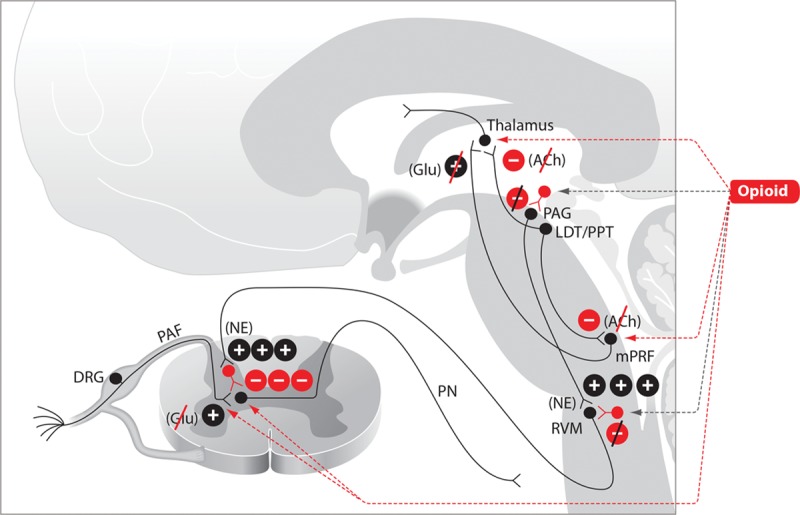
Opioids. The mechanisms of opioid-induced antinociception are produced by opioid binding to opioid receptors in the brainstem and spinal cord. Opioid-induced decrease in arousal is produced by blockade of cholinergic arousal projections from the brainstem to the thalamus and cortex. The symbol  denotes an excitatory effect. The symbol
denotes an excitatory effect. The symbol  denotes an inhibitory effect. The symbols
denotes an inhibitory effect. The symbols  and
and  denote inhibition of the indicated effects. ACh indicates acetylcholine; DRG, dorsal root ganglia; Glu, glutamate; LDT, laterodorsal tegmental area; mPRF, medial pontine reticular formation; NE, norepinephrine; PAF, peripheral afferent fiber; PAG, periaqueductal gray; PN, projection neuron; PPT, pedunculopontine tegmental area; RVM, rostral ventral medulla.
denote inhibition of the indicated effects. ACh indicates acetylcholine; DRG, dorsal root ganglia; Glu, glutamate; LDT, laterodorsal tegmental area; mPRF, medial pontine reticular formation; NE, norepinephrine; PAF, peripheral afferent fiber; PAG, periaqueductal gray; PN, projection neuron; PPT, pedunculopontine tegmental area; RVM, rostral ventral medulla.
