Figure 4.
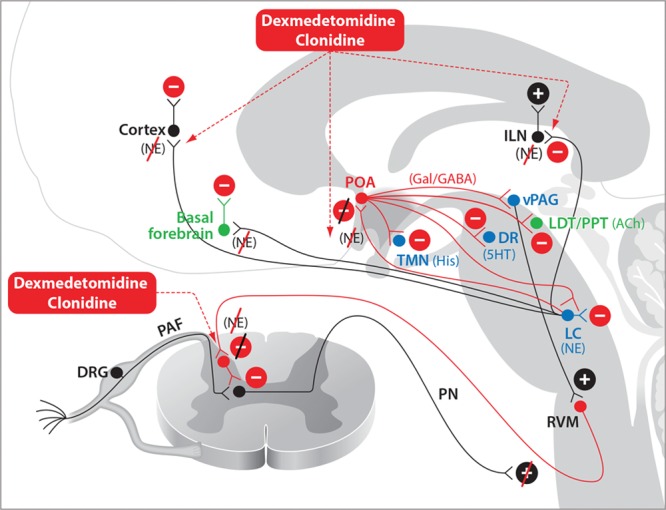
Dexmedetomidine and clonidine. Dexmedetomidine- and clonidine-induced antinociception occur primarily through enhanced inhibitory activity in the descending nociceptive pathways. Sedation induced by dexmedetomidine or clonidine and loss of consciousness induced by dexmedetomidine occur through NE-mediated disinhibition of the POA of the hypothalamus and decreased noradrenergic signaling in the thalamus and cortex. 5HT indicates serotonin; ACh, acetylcholine; DA, dopamine; DR, dorsal raphé; DRG, dorsal root ganglia; GABAA, γ-aminobutyric acid receptor subtype A; Gal, galanin; His, histamine; ILN, intralaminar nucleus of the thalamus; LC, locus coeruleus; LDT, laterodorsal tegmental area; NE, norepinephrine; PAF, peripheral afferent fiber; PN, projection neuron; POA, preoptic area; PPT, pedunculopontine tegmental area; RVM, rostral ventral medulla; TMN, tuberomammillary nucleus; vPAG, ventral periaqueductal gray.
