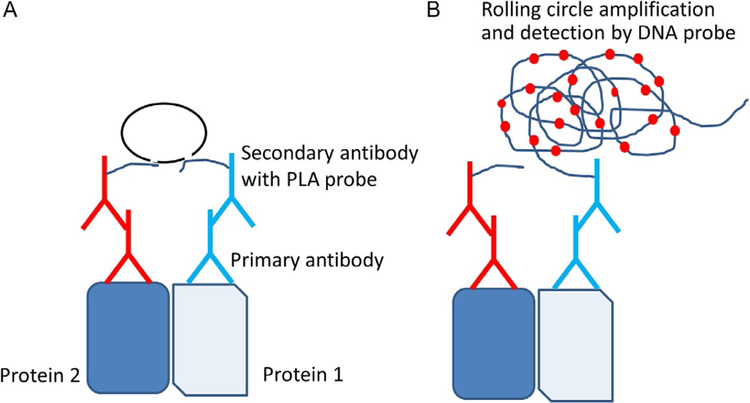
Fig. 1.
The principle of proximity ligation assay (PLA). (A) Two proteins of interest are targeted by primary antibody from different species. Corresponding secondary antibodies with DNA probes are added. If the two proteins are in proximity the hybridized DNA will be used for rolling circle amplification. (B) Amplified DNA will be detected by a DNA probe. For visualization, a DNA probe with red fluorescence is used. Each dimer of protein in cells is viewed as a red dot with a high-resolution microscope. Adapted from Trifilieff, P., Rives, M. L., Urizar, E., Piskorowski, R. A., Vishwasrao, H. D., Castrillon, J., et al. (2011). Detection of antigen interactions ex vivo by proximity ligation assay: Endogenous dopamine D2-adenosine A2A receptor complexes in the striatum. BioTechniques, 51(2), 111–118. https://doi.org/10.2144/000113719.