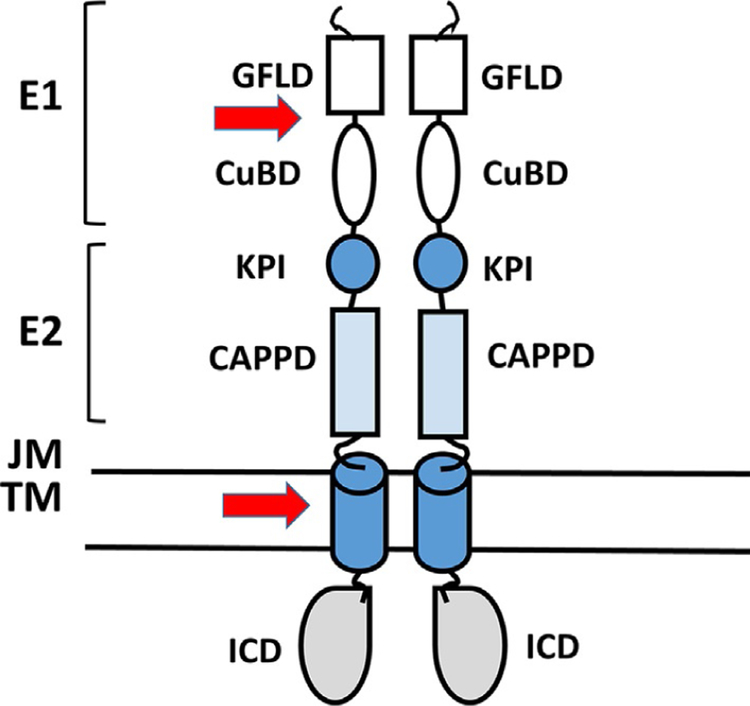
Fig. 10.
Schematic representation of different domains of APP that form homodimers. Arrows indicate the proposed dimerization regions. CAPP, central APP domain; CuBD, copper-binding region; GFLD, growth factor-like domain; ICD, intracellular domain; JM, juxtamembrane region; KPI, Kunitz protease inhibitor domain; TM, transmembrane region. Schematic diagram is drawn based on Khalifa, N. B., Van Hees, J., Tasiaux, B., Huysseune, S., Smith, S. O., Constantinescu, S. N., et al. (2010). What is the role of amyloid precursor protein dimerization? Cell Adhesion & Migration, 4(2), 268–272; Eggert, S., Midthune, B., Cottrell, B., & Koo, E. H. (2009). Induced dimerization of the amyloid precursor protein leads to decreased amyloid-beta protein production. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 284(42), 28943–28952. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.038646.