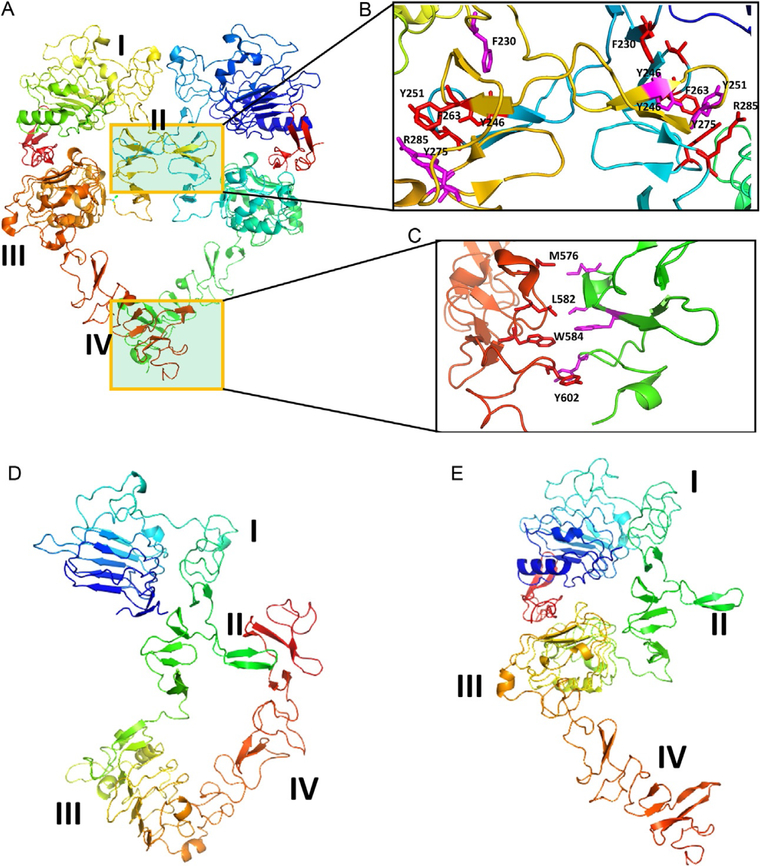
Fig. 11.
EGFR extracellular domain (ECD). (A) Homodimer (PDB ID 1NJP). Domains II and IV participate in dimerization. (B) and (C) Expanded regions of PPI of domains II and IV. Domain II region has a β-turn structure in the PPI region, forming a hydrophobic core at the interaction site. Molecules that can mimic this region are designed to inhibit PPI.Domain IV also has hydrophobic interactions that can be used to target inhibitors.(D) and (E) EGFR open (PDB ID 1NJP) and closed conformations (1NQL). Domains I–IV are labeled. In the closed conformation, domains II and IV interact, blocking the dimerization arm of domain II and forming a dimer. Notice that in open conformation, the domain IV is moved away from domain II, allowing domain II to interact with other EGFR molecules. Figure was generated using PyMol software (Schrodinger LLC, OR).